如何在go中利用二進(jìn)制對(duì)BMP文件頭進(jìn)行讀取-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
如何在go中利用二進(jìn)制對(duì)BMP文件頭進(jìn)行讀取?針對(duì)這個(gè)問(wèn)題,這篇文章詳細(xì)介紹了相對(duì)應(yīng)的分析和解答,希望可以幫助更多想解決這個(gè)問(wèn)題的小伙伴找到更簡(jiǎn)單易行的方法。
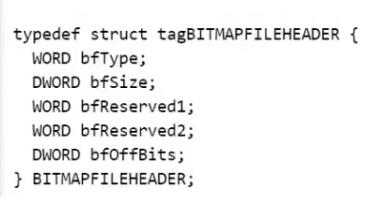
成都創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)專(zhuān)注于金堂縣企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè),響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì),商城網(wǎng)站制作。金堂縣網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司,為金堂縣等地區(qū)提供建站服務(wù)。全流程定制開(kāi)發(fā),專(zhuān)業(yè)設(shè)計(jì),全程項(xiàng)目跟蹤,成都創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)專(zhuān)業(yè)和態(tài)度為您提供的服務(wù)BMP文件頭定義:
WORD 兩個(gè)字節(jié) 16bit
DWORD 四個(gè)字節(jié) 32bit
package main
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("tim.bmp")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
//type拆成兩個(gè)byte來(lái)讀
var headA, headB byte
//Read第二個(gè)參數(shù)字節(jié)序一般windows/linux大部分都是LittleEndian,蘋(píng)果系統(tǒng)用BigEndian
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headB)
//文件大小
var size uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &size)
//預(yù)留字節(jié)
var reservedA, reservedB uint16
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedB)
//偏移字節(jié)
var offbits uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &offbits)
fmt.Println(headA, headB, size, reservedA, reservedB, offbits)
}執(zhí)行結(jié)果
66 77 196662 0 0 54
使用結(jié)構(gòu)體方式
package main
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"os"
)
type BitmapInfoHeader struct {
Size uint32
Width int32
Height int32
Places uint16
BitCount uint16
Compression uint32
SizeImage uint32
XperlsPerMeter int32
YperlsPerMeter int32
ClsrUsed uint32
ClrImportant uint32
}
func main() {
file, err := os.Open("tim.bmp")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
//type拆成兩個(gè)byte來(lái)讀
var headA, headB byte
//Read第二個(gè)參數(shù)字節(jié)序一般windows/linux大部分都是LittleEndian,蘋(píng)果系統(tǒng)用BigEndian
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &headB)
//文件大小
var size uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &size)
//預(yù)留字節(jié)
var reservedA, reservedB uint16
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedA)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &reservedB)
//偏移字節(jié)
var offbits uint32
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, &offbits)
fmt.Println(headA, headB, size, reservedA, reservedB, offbits)
infoHeader := new(BitmapInfoHeader)
binary.Read(file, binary.LittleEndian, infoHeader)
fmt.Println(infoHeader)
}執(zhí)行結(jié)果:
66 77 196662 0 0 54
&{40 256 256 1 24 0 196608 3100 3100 0 0}
補(bǔ)充:golang(Go語(yǔ)言) byte/[]byte 與 二進(jìn)制形式字符串 互轉(zhuǎn)
效果
把某個(gè)字節(jié)或字節(jié)數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)換成字符串01的形式,一個(gè)字節(jié)用8個(gè)”0”或”1”字符表示。
比如:
byte(3) –> “00000011”
[]byte{1,2,3} –> “[00000001 00000010 00000011]”
“[00000011 10000000]” –> []byte{0x3, 0x80}開(kāi)源庫(kù) biu
實(shí)際上我已經(jīng)將其封裝到一個(gè)開(kāi)源庫(kù)了(biu),其中的一個(gè)功能就能達(dá)到上述效果:
//byte/[]byte -> string
bs := []byte{1, 2, 3}
s := biu.BytesToBinaryString(bs)
fmt.Println(s) //[00000001 00000010 00000011]
fmt.Println(biu.ByteToBinaryString(byte(3))) //00000011
//string -> []byte
s := "[00000011 10000000]"
bs := biu.BinaryStringToBytes(s)
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", bs) //[]byte{0x3, 0x80}代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)
const (
zero = byte('0')
one = byte('1')
lsb = byte('[') // left square brackets
rsb = byte(']') // right square brackets
space = byte(' ')
)
var uint8arr [8]uint8
// ErrBadStringFormat represents a error of input string's format is illegal .
var ErrBadStringFormat = errors.New("bad string format")
// ErrEmptyString represents a error of empty input string.
var ErrEmptyString = errors.New("empty string")
func init() {
uint8arr[0] = 128
uint8arr[1] = 64
uint8arr[2] = 32
uint8arr[3] = 16
uint8arr[4] = 8
uint8arr[5] = 4
uint8arr[6] = 2
uint8arr[7] = 1
}
// append bytes of string in binary format.
func appendBinaryString(bs []byte, b byte) []byte {
var a byte
for i := 0; i < 8; i++ {
a = b
b <<= 1
b >>= 1
switch a {
case b:
bs = append(bs, zero)
default:
bs = append(bs, one)
}
b <<= 1
}
return bs
}
// ByteToBinaryString get the string in binary format of a byte or uint8.
func ByteToBinaryString(b byte) string {
buf := make([]byte, 0, 8)
buf = appendBinaryString(buf, b)
return string(buf)
}
// BytesToBinaryString get the string in binary format of a []byte or []int8.
func BytesToBinaryString(bs []byte) string {
l := len(bs)
bl := l*8 + l + 1
buf := make([]byte, 0, bl)
buf = append(buf, lsb)
for _, b := range bs {
buf = appendBinaryString(buf, b)
buf = append(buf, space)
}
buf[bl-1] = rsb
return string(buf)
}
// regex for delete useless string which is going to be in binary format.
var rbDel = regexp.MustCompile(`[^01]`)
// BinaryStringToBytes get the binary bytes according to the
// input string which is in binary format.
func BinaryStringToBytes(s string) (bs []byte) {
if len(s) == 0 {
panic(ErrEmptyString)
}
s = rbDel.ReplaceAllString(s, "")
l := len(s)
if l == 0 {
panic(ErrBadStringFormat)
}
mo := l % 8
l /= 8
if mo != 0 {
l++
}
bs = make([]byte, 0, l)
mo = 8 - mo
var n uint8
for i, b := range []byte(s) {
m := (i + mo) % 8
switch b {
case one:
n += uint8arr[m]
}
if m == 7 {
bs = append(bs, n)
n = 0
}
}
return
}關(guān)于如何在go中利用二進(jìn)制對(duì)BMP文件頭進(jìn)行讀取問(wèn)題的解答就分享到這里了,希望以上內(nèi)容可以對(duì)大家有一定的幫助,如果你還有很多疑惑沒(méi)有解開(kāi),可以關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道了解更多相關(guān)知識(shí)。
當(dāng)前名稱(chēng):如何在go中利用二進(jìn)制對(duì)BMP文件頭進(jìn)行讀取-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
URL鏈接:http://www.chinadenli.net/article30/dhsgso.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供品牌網(wǎng)站制作、網(wǎng)站維護(hù)、商城網(wǎng)站、品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)、自適應(yīng)網(wǎng)站、動(dòng)態(tài)網(wǎng)站
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶(hù)投稿、用戶(hù)轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
猜你還喜歡下面的內(nèi)容
- 如何在Java中使用sun.misc.Unsafe類(lèi)-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- docker19.03如何使用NVIDIA顯卡-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- LinuxCentOS服務(wù)器搭建與初始化配置的方法-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- 如何安裝R語(yǔ)言3.6.3-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- Android布局像素單位-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- php刪除多維數(shù)組的方法-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- Zendstudio導(dǎo)入項(xiàng)目報(bào)錯(cuò):overlapsthe-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站網(wǎng)頁(yè)表現(xiàn)設(shè)計(jì)方法 2020-07-13
- 電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站的運(yùn)行管理 2023-01-28
- 北京網(wǎng)站建設(shè),如何設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站? 2021-04-15
- 電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)要掌握這些技巧 2021-03-29
- ERP管理系統(tǒng)助力企業(yè)電子商務(wù),核心模塊如何操作? 2022-03-19
- 如何使B2C電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)得更人性化 2022-01-30
- 電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站制作公司創(chuàng)新互聯(lián) 2021-09-12
- 成都電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)行業(yè)就是金礦! 2016-08-05
- 沈陽(yáng)網(wǎng)站建設(shè):電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站的三大發(fā)展趨勢(shì) 2023-03-18
- 電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站購(gòu)物車(chē)如何運(yùn)行? 2022-05-01
- 新樂(lè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)-如何規(guī)劃電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站呢? 2021-11-19
- 電子商務(wù)與網(wǎng)絡(luò)營(yíng)銷(xiāo)的關(guān)系 2015-11-09