Android如何仿IOS實現(xiàn)上拉下拉彈性效果-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
這篇文章主要介紹了Android如何仿IOS實現(xiàn)上拉下拉彈性效果,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
用過iphone的朋友相信都體驗過頁面上拉下拉有一個彈性的效果,使用起來用戶體驗很好;Android并沒有給我們封裝這樣一個效果,我們來看下在Android里如何實現(xiàn)這個效果。先看效果,感覺有些時候還是蠻實用的。
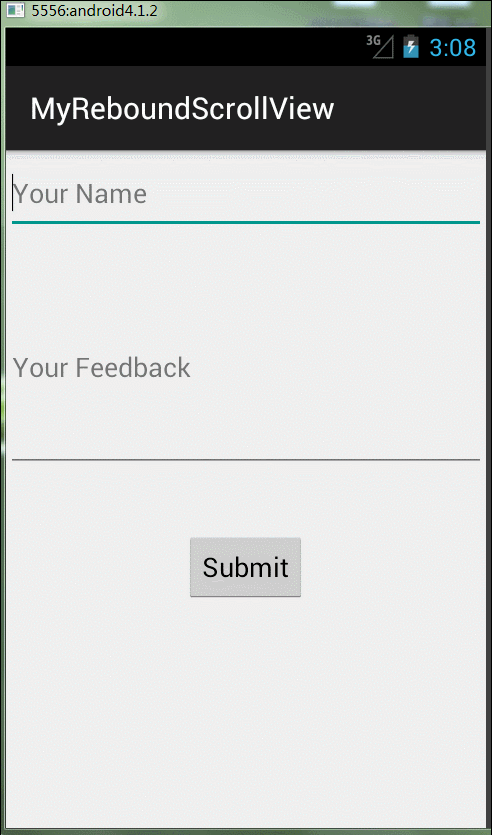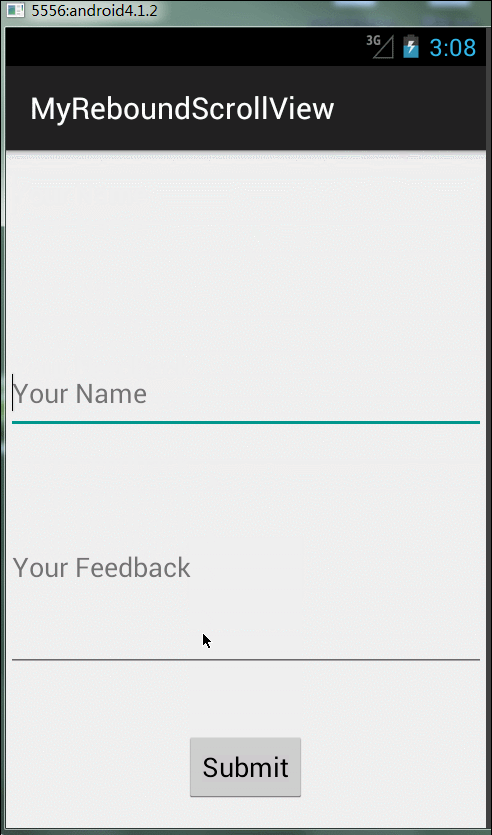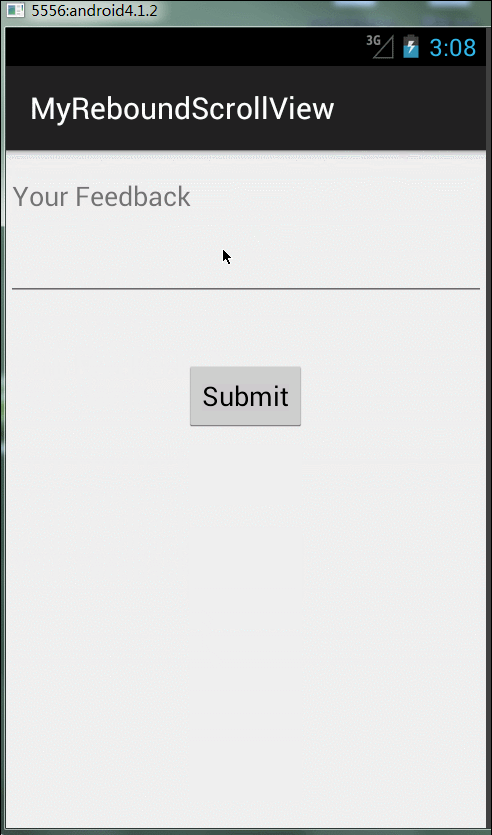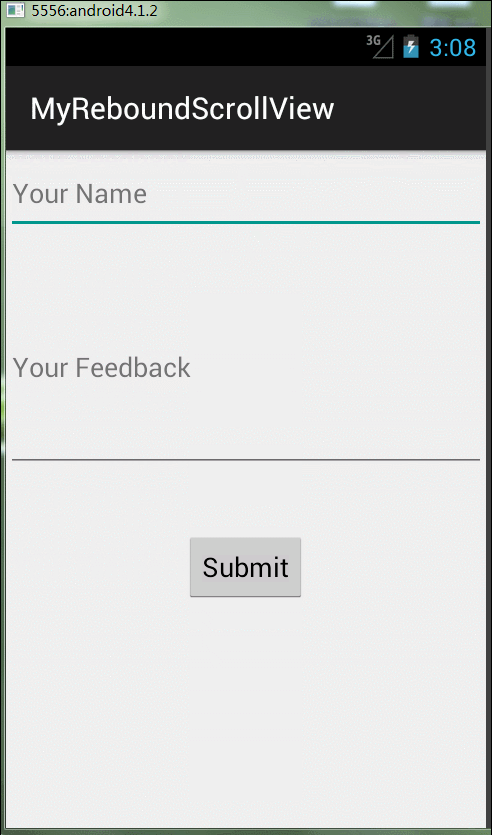
思路:其實原理很簡單,實現(xiàn)一個自定義的Scrollview方法(來自網(wǎng)上大神),然后在布局文件中使用自定義方法Scrollview就可以了。
代碼:
自定義View,繼承自Scrollview。MyReboundScrollView類
package com.wj.myreboundscrollview.customview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.TranslateAnimation;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
//仿ios可上提下拉的ScrollView
public class MyReboundScrollView extends ScrollView {
private static final String TAG = "ElasticScrollView";
//移動因子, 是一個百分比, 比如手指移動了100px, 那么View就只移動50px
//目的是達(dá)到一個延遲的效果
private static final float MOVE_FACTOR = 0.5f;
//松開手指后, 界面回到正常位置需要的動畫時間
private static final int ANIM_TIME = 100;
//ScrollView的子View, 也是ScrollView的唯一一個子View
private View contentView;
//手指按下時的Y值, 用于在移動時計算移動距離
//如果按下時不能上拉和下拉, 會在手指移動時更新為當(dāng)前手指的Y值
private float startY;
//用于記錄正常的布局位置
private Rect originalRect = new Rect();
//手指按下時記錄是否可以繼續(xù)下拉
private boolean canPullDown = false;
//手指按下時記錄是否可以繼續(xù)上拉
private boolean canPullUp = false;
//在手指滑動的過程中記錄是否移動了布局
private boolean isMoved = false;
public MyReboundScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyReboundScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onFinishInflate() {
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
contentView = getChildAt(0);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
if(contentView == null) return;
//ScrollView中的唯一子控件的位置信息, 這個位置信息在整個控件的生命周期中保持不變
originalRect.set(contentView.getLeft(), contentView.getTop(), contentView
.getRight(), contentView.getBottom());
}
//在觸摸事件中, 處理上拉和下拉的邏輯
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (contentView == null) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
int action = ev.getAction();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
//判斷是否可以上拉和下拉
canPullDown = isCanPullDown();
canPullUp = isCanPullUp();
//記錄按下時的Y值
startY = ev.getY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
if(!isMoved) break; //如果沒有移動布局, 則跳過執(zhí)行
// 開啟動畫
TranslateAnimation anim = new TranslateAnimation(0, 0, contentView.getTop(),
originalRect.top);
anim.setDuration(ANIM_TIME);
contentView.startAnimation(anim);
// 設(shè)置回到正常的布局位置
contentView.layout(originalRect.left, originalRect.top,
originalRect.right, originalRect.bottom);
//將標(biāo)志位設(shè)回false
canPullDown = false;
canPullUp = false;
isMoved = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//在移動的過程中, 既沒有滾動到可以上拉的程度, 也沒有滾動到可以下拉的程度
if(!canPullDown && !canPullUp) {
startY = ev.getY();
canPullDown = isCanPullDown();
canPullUp = isCanPullUp();
break;
}
//計算手指移動的距離
float nowY = ev.getY();
int deltaY = (int) (nowY - startY);
//是否應(yīng)該移動布局
boolean shouldMove =
(canPullDown && deltaY > 0) //可以下拉, 并且手指向下移動
|| (canPullUp && deltaY< 0) //可以上拉, 并且手指向上移動
|| (canPullUp && canPullDown); //既可以上拉也可以下拉(這種情況出現(xiàn)在ScrollView包裹的控件比ScrollView還小)
if(shouldMove){
//計算偏移量
int offset = (int)(deltaY * MOVE_FACTOR);
//隨著手指的移動而移動布局
contentView.layout(originalRect.left, originalRect.top + offset,
originalRect.right, originalRect.bottom + offset);
isMoved = true; //記錄移動了布局
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
//判斷是否滾動到頂部
private boolean isCanPullDown() {
return getScrollY() == 0 ||
contentView.getHeight() < getHeight() + getScrollY();
}
//判斷是否滾動到底部
private boolean isCanPullUp() {
return contentView.getHeight() <= getHeight() + getScrollY();
}
}代碼注釋非常清楚。
布局文件直接使用
<com.wj.myreboundscrollview.customview.MyReboundScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" android:orientation="vertical"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="12dip" android:hint="Your Name"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_feedback" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="32dip" android:hint="Your Feedback" android:lines="5"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_submit" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:layout_marginTop="42dip" android:text="Submit" android:onClick="submit"/> </LinearLayout> </com.wj.myreboundscrollview.customview.MyReboundScrollView>
這里直接在外層包裹實現(xiàn)。注意,因為Myreboundscrollview是繼承自Scrollview,因此要遵循Scrollview的使用原則,里面只能包含一個LinearLayout,所以無論里面多門復(fù)雜的布局,最后我們都要將其包含在一個LinearLayout中。
ok,功能實現(xiàn),效果也演示,具體需要使用直接拿來用就可以。
感謝你能夠認(rèn)真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Android如何仿IOS實現(xiàn)上拉下拉彈性效果”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道,更多相關(guān)知識等著你來學(xué)習(xí)!
當(dāng)前名稱:Android如何仿IOS實現(xiàn)上拉下拉彈性效果-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
瀏覽路徑:http://www.chinadenli.net/article26/dccdjg.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供搜索引擎優(yōu)化、做網(wǎng)站、企業(yè)網(wǎng)站制作、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計公司、網(wǎng)站營銷、云服務(wù)器
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
猜你還喜歡下面的內(nèi)容
- SparkBroadcast運行機(jī)制解密(42)-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- SAPS/4HANA里怎么創(chuàng)建Customer主數(shù)據(jù)以及執(zhí)行后續(xù)處理-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- vue中vuex的五個屬性和基本用法-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- Hybrid實驗-同一網(wǎng)段下,不同VLAN之間的互訪-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- es云服務(wù)器異常問題如何解決-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- 如何在Jupyter中重新導(dǎo)入特定的Python文件-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
- AWSCloudWatchAgent的配置和使用-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計的頁腳樣式是什么 2021-06-20
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計如何在同行業(yè)中脫穎而出? 2016-01-18
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計如何達(dá)到展示目的 2013-09-04
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計中運用到的首頁色彩和框架 2023-02-16
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計對企業(yè)來說有什么意義 2021-10-27
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計開發(fā)要點 2016-11-09
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計的四大原則 2022-12-12
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計要遵守哪些原則 2023-03-11
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計應(yīng)該考慮的問題有哪些? 2023-03-23
- 深圳品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計公司 2014-05-13
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計四大核心制作要素 2022-08-15
- 品牌網(wǎng)站設(shè)計-好的用戶體驗更容易留住用戶 2022-04-30