如何從一個組件的實現(xiàn)來深刻理解JS中的繼承
今天就跟大家聊聊有關(guān)如何從一個組件的實現(xiàn)來深刻理解JS中的繼承,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結(jié)了以下內(nèi)容,希望大家根據(jù)這篇文章可以有所收獲。
成都創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)公司企業(yè)建站,10余年網(wǎng)站建設(shè)經(jīng)驗,專注于網(wǎng)站建設(shè)技術(shù),精于網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計,有多年建站和網(wǎng)站代運營經(jīng)驗,設(shè)計師為客戶打造網(wǎng)絡(luò)企業(yè)風格,提供周到的建站售前咨詢和貼心的售后服務(wù)。對于成都做網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)站制作中不同領(lǐng)域進行深入了解和探索,創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)在網(wǎng)站建設(shè)中充分了解客戶行業(yè)的需求,以靈動的思維在網(wǎng)頁中充分展現(xiàn),通過對客戶行業(yè)精準市場調(diào)研,為客戶提供的解決方案。
其實,無論是寫什么語言的程序員,最終的目的,都是把產(chǎn)品或代碼封裝到一起,提供接口,讓使用者很舒適的實現(xiàn)功能。所以對于我來說,往往頭疼的不是寫代碼,而是寫注釋和文檔!如果接口很亂,肯定會頭疼一整天。
JavaScript 最初是以 Web 腳本語言面向大眾的,盡管現(xiàn)在出了服務(wù)器端的 nodejs,但是單線程的性質(zhì)還沒有變。對于一個 Web 開發(fā)人員來說,能寫一手漂亮的組件極為重要。GitHub 上那些開源且 stars 過百的 Web 項目或組件,可讀性肯定非常好。
從一個例子來學習寫組件
組件教程的參考來自于 GitHub 上,通俗易懂,鏈接。
要實現(xiàn)下面這個功能,對一個 input 輸入框的內(nèi)容進行驗證,只有純數(shù)字和字母的組合才是被接受的,其他都返回 failed:

全局變量寫法
這種寫法完全沒有約束,基本所有人都會,完全沒啥技巧:
// html <input type="text" id="input"/> // javascript var input = document.getElementById("input"); function getValue(){ return input.value; } function render(){ var value = getValue(); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } } input.addEventListener('keyup', function(){ render(); });缺點自然不用多說,變量沒有任何隔離,嚴重污染全局變量,雖然可以達到目的,但極不推薦這種寫法。
對象隔離作用域
鑒于以上寫法的弊端,我們用對象來隔離變量和函數(shù):
var obj = { input: null, // 初始化并提供入口調(diào)用方法 init: function(config){ this.input = document.getElementById(config.id); this.bind(); //鏈式調(diào)用 return this; }, // 綁定 bind: function(){ var self = this; this.input.addEventListener('keyup', function(){ self.render(); }); }, getValue: function(){ return this.input.value; }, render: function(){ var value = this.getValue(); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } } } window.onload = function(){ obj.init({id: "input"}); }相對于開放式的寫法,上面的這個方法就比較清晰了。有初始化,有內(nèi)部函數(shù)和變量,還提供入口調(diào)用方法。
新手能實現(xiàn)上面的方法已經(jīng)很不錯了,還記得當初做百度前端學院題目的時候,基本就是用對象了。
不過這種方法仍然有弊端。obj 對象中的方法都是公開的,并不是私有的,其他人寫的代碼可以隨意更改這些內(nèi)容。當多人協(xié)作或代碼量很多時,又會產(chǎn)生一系列問題。
函數(shù)閉包的寫法
var fun = (function(){ var _bind = function(obj){ obj.input.addEventListener('keyup', function(){ obj.render(); }); } var _getValue = function(obj){ return obj.input.value; } var InputFun = function(config){}; InputFun.prototype.init = function(config){ this.input = document.getElementById(config.id); _bind(this); return this; } InputFun.prototype.render = function(){ var value = _getValue(this); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } } return InputFun; })(); window.onload = function(){ new fun().init({id: 'input'}); }函數(shù)閉包寫法的好處都在自執(zhí)行的閉包里,不會受到外面的影響,而且提供給外面的方法包括 init 和 render。比如我們可以像 JQuery 那樣,稍微對其改造一下:
var $ = function(id){ // 這樣子就不用每次都 new 了 return new fun().init({'id': id}); } window.onload = function(){ $('input'); }還沒有涉及到原型,只是簡單的閉包。
基本上,這已經(jīng)是一個合格的寫法了。
面向?qū)ο?/strong>
雖然上面的方法以及夠好了,但是我們的目的,是為了使用面向?qū)ο蟆C嫦驅(qū)ο笠恢币詠矶际潜徽J為***的編程方式,如果每個人的代碼風格都相似,維護、查看起來就非常的方便。
但是,我想在介紹面向?qū)ο笾埃葋砘貞浺幌?JS 中的繼承(實現(xiàn)我們放到***再說)。
入門級的面向?qū)ο?/strong>
提到繼承,我首先想到的就是用 new 來實現(xiàn)。還是以例子為主吧,人->學生->小學生,在 JS 中有原型鏈這么一說,__proto__ 和 prototype ,對于原型鏈就不過多闡述,如果不懂的可以自己去查閱一些資料。
在這里,我還是要說明一下 JS 中的 new 構(gòu)造,比如 var student = new Person(name),實際上有三步操作:
var student = {}; student.__proto__ = Person.prototype; Person.call(student, name)得到的 student 是一個對象,__proto__執(zhí)行 Person 的 prototype,Person.call 相當于 constructor。
function Person(name){ this.name = name; } Person.prototype.Say = function(){ console.log(this.name + ' can say!'); } var ming = new Person("xiaoming"); console.log(ming.__proto__ == Person.prototype) //true new的第二步結(jié)果 console.log(ming.name) // 'xiaoming' new 的第三步結(jié)果 ming.Say() // 'xiaoming can say!' proto 向上追溯的結(jié)果利用 __proto__ 屬性的向上追溯,可以實現(xiàn)一個基于原型鏈的繼承。
function Person(name){ this.name = name; } Person.prototype.Say = function(){ console.log(this.name + ' can say!'); } function Student(name){ Person.call(this, name); //Person 的屬性賦值給 Student } Student.prototype = new Person(); //順序不能反,要在最前面 Student.prototype.DoHomeWork = function(){ console.log(this.name + ' can do homework!'); } var ming = new Student("xiaoming"); ming.DoHomeWork(); //'xiaoming can do homework!' ming.Say(); //'xiaoming can say!'大概剛認識原型鏈的時候,我也就只能寫出這樣的水平了,我之前的文章。
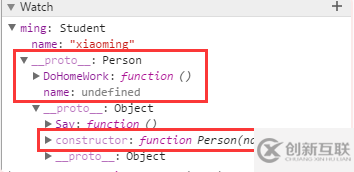
打開調(diào)試工具,看一下 ming 都有哪些東西:
ming name: "xiaoming" __proto__: Person DoHomeWork: () name: undefined //注意這里多了一個 name 屬性 __proto__: Object Say: () constructor: Person(name) __proto__: Object
當調(diào)用 ming.Say() 的時候,剛好 ming.__proto__.__proto__ 有這個屬性,這就是鏈式調(diào)用的原理,一層一層向下尋找。
這就是最簡單的繼承了。
面向?qū)ο蟮倪M階
來看一看剛才那種做法的弊端。
沒有實現(xiàn)傳統(tǒng)面向?qū)ο笤撚械?super 方法來調(diào)用父類方法,鏈式和 super 方法相比還是有一定缺陷的;
造成過多的原型屬性(name),constructor 丟失(constructor 是一個非常重要的屬性,MDN)。
因為鏈式是一層層向上尋找,知道找到為止,很明顯 super 直接調(diào)用父類更具有優(yōu)勢。
// 多了原型屬性 console.log(ming.__proto__) // {name: undefined}為什么會多一個 name,原因是因為我們執(zhí)行了 Student.prototype = new Person();,而 new 的第三步會執(zhí)行一個 call 的函數(shù),會使得 Student.prototype.name = undefined,恰好 ming.__proto__ 指向 Student 的 prototype,用了 new 是無法避免的。
// 少了 constructor console.log(ming.constructor == Person) //true console.log(ming.constructor == Student) // false
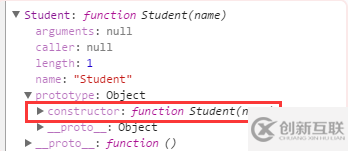
這也很奇怪,明明 ming 是繼承與 Student,卻返回 false,究其原因,Student.prototype 的 constructor 方法丟失,向上找到了Student.prototype.__proto__ 的 constructor 方法。
再找原因,這句話導致了 Student.prototype 的 constructor 方法丟失:
Student.prototype = new Person();
在這句話之前打一個斷點,曾經(jīng)是有的,只是被替換掉了:
找到了問題所在,現(xiàn)在來改進:
// fn 用來排除多余的屬性(name) var fn = function(){}; fn.prototype = Person.prototype; Student.prototype = new fn(); // 重新添上 constructor 屬性 Student.prototype.constructor = Student;用上面的繼承代碼替換掉之前的 Student.prototype = new Person();
面向?qū)ο蟮姆庋b
我們不能每一次寫代碼的時候都這樣寫這么多行來繼承吧,所以,于情于理,還是來進行簡單的包裝:
function classInherit(subClass, parentClass){ var fn = function(){}; fn.prototype = parentClass.prototype; subClass.prototype = new fn(); subClass.prototype.constructor = subClass; } classInherit(Student, Person);哈哈,所謂的包裝,就是重抄一下代碼。
進一步完善面向?qū)ο?/strong>
上面的問題只是簡單的解決了多余屬性和 constructor 丟失的問題,而 supper 問題仍然沒有改進。
舉個栗子,來看看 supper 的重要,每個人都會睡覺,sleep 函數(shù)是人的一個屬性,學生分為小學生和大學生,小學生晚上 9 點睡覺,大學生 12 點睡覺,于是:
Person.prototype.Sleep = function(){ console.log('Sleep!'); } function E_Student(){}; //小學生 function C_Student(){}; //大學生 classInherit(E_Student, Person); classInherit(C_Student, Person); //重寫 Sleep 方法 E_Student.prototype.Sleep = function(){ console.log('Sleep!'); console.log('Sleep at 9 clock'); } C_Student.prototype.Sleep = function(){ console.log('Sleep!'); console.log('Sleep at 12 clock'); }對于 Sleep 方法,顯得比較混亂,而我們想要通過 supper,直接調(diào)用父類的函數(shù):
E_Student.prototype.Sleep = function(){ this._supper(); //supper 方法 console.log('Sleep at 9 clock'); } C_Student.prototype.Sleep = function(){ this._supper(); //supper 方法 console.log('Sleep at 12 clock'); }不知道對 supper 的理解正不正確,總感覺怪怪的,歡迎指正!
來看下 JQuery 之父是如何 class 的面向?qū)ο螅脑谶@,源碼如下。
/* Simple JavaScript Inheritance * By John Resig http://ejohn.org/ * MIT Licensed. */ // Inspired by base2 and Prototype (function(){ // initializing 開關(guān)很巧妙的來實現(xiàn)調(diào)用原型而不構(gòu)造,還有回掉 var initializing = false, fnTest = /xyz/.test(function(){xyz;}) ? /\b_super\b/ : /.*/; // The base Class implementation (does nothing) // 全局,this 指向 window,***的父類 this.Class = function(){}; // Create a new Class that inherits from this class // 繼承的入口 Class.extend = function(prop) { //保留當前類,一般是父類的原型 var _super = this.prototype; // Instantiate a base class (but only create the instance, // don't run the init constructor) //開關(guān) 用來使原型賦值時不調(diào)用真正的構(gòu)成流程 initializing = true; var prototype = new this(); initializing = false; // Copy the properties over onto the new prototype for (var name in prop) { // Check if we're overwriting an existing function //對函數(shù)判斷,將屬性套到子類上 prototype[name] = typeof prop[name] == "function" && typeof _super[name] == "function" && fnTest.test(prop[name]) ? (function(name, fn){ //用閉包來存儲 return function() { var tmp = this._super; // Add a new ._super() method that is the same method // but on the super-class this._super = _super[name]; // The method only need to be bound temporarily, so we // remove it when we're done executing //實現(xiàn)同名調(diào)用 var ret = fn.apply(this, arguments); this._super = tmp; return ret; }; })(name, prop[name]) : prop[name]; } // 要返回的子類 function Class() { // All construction is actually done in the init method if ( !initializing && this.init ) this.init.apply(this, arguments); } //前面介紹過的,繼承 Class.prototype = prototype; Class.prototype.constructor = Class; Class.extend = arguments.callee; return Class; }; })();這個時候就可以很輕松的實現(xiàn)面向?qū)ο螅褂萌缦拢?/p>
var Person = Class.extend({ init: function(name){ this.name = name; }, Say: function(name){ console.log(this.name + ' can Say!'); }, Sleep: function(){ console.log(this.name + ' can Sleep!'); } }); var Student = Person.extend({ init: function(name){ this._super('Student-' + name); }, Sleep: function(){ this._super(); console.log('And sleep early!'); }, DoHomeWork: function(){ console.log(this.name + ' can do homework!'); } }); var p = new Person('Li'); p.Say(); //'Li can Say!' p.Sleep(); //'Li can Sleep!' var ming = new Student('xiaoming'); ming.Say(); //'Student-xiaoming can Say!' ming.Sleep();//'Student-xiaoming can Sleep!' // 'And sleep early!' ming.DoHomeWork(); //'Student-xiaoming can do homework!'除了 John Resig 的 supper 方法,很多人都做了嘗試,不過我覺得 John Resig 的實現(xiàn)方式非常的妙,也比較貼近 supper 方法,我本人也用源碼調(diào)試了好幾個小時,才勉強能理解。John Resig 的頭腦真是令人佩服。
ES6 中的 class
在 JS 中,class 從一開始就屬于關(guān)鍵字,在 ES6 終于可以使用 class 來定義類。比如:
class Point { constructor(x, y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } toString(){ return '(' + this.x + ',' + this.y + ')'; } } var p = new Point(3, 4); console.log(p.toString()); //'(3,4)'更多有關(guān)于 ES6 中類的使用請參考阮一峰老師的 Class基本語法。
其實 ES6 中的 class 只是寫對象原型的時候更方便,更像面向?qū)ο螅琧lass 的功能 ES5 完全可以做到,比如就上面的例子:
typeof Point; //'function' Point.prototype; /* |Object |--> constructor: function (x, y) |--> toString: function() |--> __proto__: Object */
和用 ES5 實現(xiàn)的真的沒有什么差別,反而現(xiàn)在流行的一些庫比 ES6 的 class 能帶來更好的效益。
回到最開始的組件問題
那么,說了這么多面向?qū)ο螅F(xiàn)在回到最開始的那個組件的實現(xiàn)——如何用面向?qū)ο髞韺崿F(xiàn)。
還是利用 John Resig 構(gòu)造 class 的方法:
var JudgeInput = Class.extend({ init: function(config){ this.input = document.getElementById(config.id); this._bind(); }, _getValue: function(){ return this.input.value; }, _render: function(){ var value = this._getValue(); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } }, _bind: function(){ var self = this; self.input.addEventListener('keyup', function(){ self._render(); }); } }); window.onload = function(){ new JudgeInput({id: "input"}); }但是,這樣子,基本功能算是實現(xiàn)了,關(guān)鍵是不好擴展,沒有面向?qū)ο蟮木琛K裕槍δ壳暗那闆r,我們準備建立一個 Base 基類,init 表示初始化,render 函數(shù)表示渲染,bind 函數(shù)表示綁定,destory 用來銷毀,同時 get、set 方法提供獲得和更改屬性:
var Base = Class.extend({ init: function(config){ this._config = config; this.bind(); }, get: function(key){ return this._config[key]; }, set: function(key, value){ this._config[key] = value; }, bind: function(){ //以后構(gòu)造 }, render: function(){ //以后構(gòu)造 }, destory: function(){ //定義銷毀方法 } });基于這個 Base,我們修改 JudgeInput 如下:
var JudgeInput = Base.extend({ _getValue: function(){ return this.get('input').value; }, bind: function(){ var self = this; self.get('input').addEventListener('keyup', function(){ self.render(); }); }, render: function(){ var value = this._getValue(); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } } }); window.onload = function(){ new JudgeInput({input: document.getElementById("input")}); }比如,我們后期修改了判斷條件,只有當長度為 5-10 的時候才會返回 success,這個時候能很快定位到 JudgeInput 的 render 函數(shù):
render: function(){ var value = this._getValue(); if(!document.getElementById("show")){ var append = document.createElement('span'); append.setAttribute("id", "show"); input.parentNode.appendChild(append); } var show = document.getElementById("show"); //修改正則即可 if(/^[0-9a-zA-Z]{5,10}$/.exec(value)){ show.innerHTML = 'Pass!'; }else{ show.innerHTML = 'Failed!'; } }以我目前的能力,只能理解到這里了。
關(guān)于一個組件的寫法,從入門級到最終版本,一波三折,不僅要考慮代碼的實用性,還要兼顧后期維護。JS 中實現(xiàn)面向?qū)ο螅瑒偨佑| JS 的時候,我能用簡單的原型鏈來實現(xiàn),后來看了一些文章,發(fā)現(xiàn)了不少問題,在看 John Resig 的 Class,感觸頗深。還好,現(xiàn)在目的是實現(xiàn)了。
看完上述內(nèi)容,你們對如何從一個組件的實現(xiàn)來深刻理解JS中的繼承有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關(guān)內(nèi)容,請關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
網(wǎng)頁名稱:如何從一個組件的實現(xiàn)來深刻理解JS中的繼承
文章路徑:http://www.chinadenli.net/article46/gpcseg.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供標簽優(yōu)化、網(wǎng)站設(shè)計公司、靜態(tài)網(wǎng)站、電子商務(wù)、網(wǎng)站營銷、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計公司
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 品牌網(wǎng)站制作怎么建設(shè)更高效 2021-08-27
- 高端品牌網(wǎng)站制作策劃方案 2021-10-09
- 湛江品牌網(wǎng)站制作:做好品牌網(wǎng)站制作方案有哪些要點? 2021-12-23
- 企業(yè)品牌網(wǎng)站制作要注重哪些問題? 2023-04-18
- 品牌網(wǎng)站制作之搜索引擎營銷 2021-11-17
- 集團型網(wǎng)站建設(shè)品牌網(wǎng)站制作設(shè)計 2020-12-03
- 品牌網(wǎng)站制作的價格為什么那么高呢? 2016-10-28
- 周口品牌網(wǎng)站建設(shè):在品牌網(wǎng)站制作的過程中有哪些值得注意的問題? 2021-09-10
- 品牌網(wǎng)站制作好方法好步驟有哪些? 2022-06-27
- 中小企業(yè)品牌網(wǎng)站制作與塑造 2021-12-06
- 為什么高端品牌網(wǎng)站制作公司越來越少了 2016-11-12
- 品牌網(wǎng)站制作解決方案 2016-09-12