ASP.NET中EntLib出現(xiàn)異常的處理方法
今天小編給大家分享的是ASP.NET中EntLib出現(xiàn)異常的處理方法,相信很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,所以給大家總結(jié)了以下內(nèi)容,一起往下看吧。一定會(huì)有所收獲的哦。
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)主要從事網(wǎng)站制作、網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、網(wǎng)頁(yè)設(shè)計(jì)、企業(yè)做網(wǎng)站、公司建網(wǎng)站等業(yè)務(wù)。立足成都服務(wù)遷安,十余年網(wǎng)站建設(shè)經(jīng)驗(yàn),價(jià)格優(yōu)惠、服務(wù)專業(yè),歡迎來(lái)電咨詢建站服務(wù):18980820575
EntLib的異常處理應(yīng)用塊(Exception Handling Application Block)是一個(gè)不錯(cuò)的異常處理框架,它使我們可以采用配置的方式來(lái)定義異常處理策略。而ASP.NET MVC是一個(gè)極具可擴(kuò)展開發(fā)框架,在這篇文章中我將通過(guò)它的擴(kuò)展實(shí)現(xiàn)與EntLib的集成,并提供一個(gè)完整的解決異常處理解決方案。
一、基本異常處理策略
我們首先來(lái)討論我們的解決方案具體采用的異常處理策略:
對(duì)于執(zhí)行Controller的某個(gè)Action方法拋出的異常,我們會(huì)按照指定配置策略進(jìn)行處理。我們可以采取日志記錄、異常替換和封裝這些常用的異常處理方式;
對(duì)于處理后的異常,如果異常處理策略規(guī)定需要將其拋出,則會(huì)自動(dòng)重定向到與異常類型匹配的出錯(cuò)頁(yè)面。我們會(huì)維護(hù)一個(gè)異常類型和Error View的匹配關(guān)系;
對(duì)于處理后的異常,如果異常處理策略規(guī)定不需要將其拋出,則會(huì)執(zhí)行與當(dāng)前Action操作相匹配的錯(cuò)誤處理Action進(jìn)行處理。異常處理Action方法默認(rèn)采用“On{Action}Error”這樣的命名規(guī)則,而當(dāng)前上下文會(huì)與異常處理操作方法的參數(shù)進(jìn)行綁定。除次之外,我們會(huì)設(shè)置當(dāng)前ModelState的錯(cuò)誤信息;
如果用戶不曾定義相應(yīng)的異常處理Action,依然采用“錯(cuò)誤頁(yè)面重定向”方式進(jìn)行異常處理。
二、通過(guò)自定義Action處理異常
為了讓讀者對(duì)上面介紹的異常處理頁(yè)面有一個(gè)深刻的理解,我們來(lái)進(jìn)行一個(gè)實(shí)例演示。該實(shí)例用于模擬用戶登錄,我們定義了如下一個(gè)只包含用戶名和密碼兩個(gè)屬性的Model:LoginInfoModel。
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models
{
public class LoginInfo
{
[Display(Name ="User Name")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "User Name is manadatory!")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Password")]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Password is manadatory!")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}我們定義了如下一個(gè)AccountController,它是我們自定義的BaseController的子類。AccountController在構(gòu)造的時(shí)候調(diào)用基類構(gòu)造函數(shù)指定的參數(shù)代表異常處理策略的配置名稱。SignIn方法代表用于進(jìn)行“登錄”的操作,而OnSignInError就表示該操作對(duì)應(yīng)的異常處理操作。如果在SignIn操作中拋出的異常經(jīng)過(guò)處理后無(wú)需再拋出,則會(huì)通過(guò)調(diào)用OnSignInError,而此時(shí)ModelState已經(jīng)被設(shè)置了相應(yīng)的錯(cuò)誤消息。
public class AccountController BaseController
{
public AccountController()
base("myPolicy")
{ }
public ActionResult SignIn()
{
return View(new LoginInfo());
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult SignIn(LoginInfo loginInfo)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
if (loginInfo.UserName != "Foo")
{
throw new InvalidUserNameException();
}
if (loginInfo.Password != "password")
{
throw new UserNamePasswordNotMatchException();
}
ViewBag.Message = "Authentication Succeeds!";
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = loginInfo.UserName });
}
public ActionResult OnSignInError(string userName)
{
return this.View(new LoginInfo { UserName = userName });
}
}具體定義在SignIn操作方法中的認(rèn)證邏輯是這樣的:如果用戶名不是“Foo”則拋出InvalidUserNameException異常;如果密碼不是“password”則拋出UserNamePasswordNotMatchException異常。下面是SignIn操作對(duì)應(yīng)的View的定義:
@model Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.LoginInfo
@{
ViewBag.Title = "SignIn";
}
@Html.ValidationSummary()
@if (ViewBag.Messages != null)
{
@ViewBag.Messages
}
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.EditorForModel()
<input type="submit" value="SignIn" />
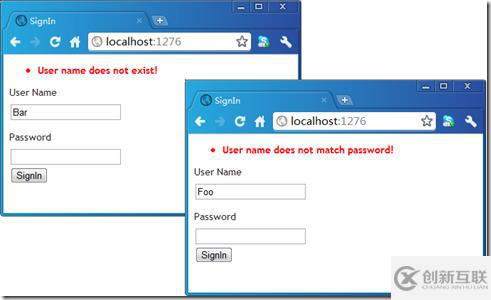
}在AccountController初始化時(shí)指定的異常處理策略“myPolicy”定義在如下的配置中。我們專門針對(duì)SignIn操作方法拋出的InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException進(jìn)行了處理,而ErrorMessageSettingHandler是我們自定義的異常處理器,它僅僅用于設(shè)置錯(cuò)誤消息。如下面的代碼片斷所示,如果上述的這兩種類型的異常被拋出,最終的錯(cuò)誤消息會(huì)被指定為“User name does not exist!”和“User name does not match password!”。
<exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not exist!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="None">
<exceptionHandlers>
<add name="ErrorMessageSettingHandler"
type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.ErrorMessageSettingHandler, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorMessage="User name does not match password!"/>
</exceptionHandlers>
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling>現(xiàn)在我們通過(guò)路由映射將AccountController和Sign設(shè)置為默認(rèn)Controller和Action后,開啟我們的應(yīng)用程序。在輸入錯(cuò)誤的用戶名和錯(cuò)誤明碼的情況下在ValidationSummary中將自動(dòng)得到相應(yīng)的錯(cuò)誤消息。
三、通過(guò)配置的Error View處理異常
在上面的配置中,針對(duì)InvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException這兩種異常類型的配置策略都將PostHandlingAction屬性設(shè)置為“None”,意味著不會(huì)將原來(lái)的異常和處理后的異常進(jìn)行重新拋出。現(xiàn)在我們將該屬性設(shè)置為“ThrowNewException”,意味著我們會(huì)將處理后的異常重新拋出來(lái)。
<exceptionHandling>
<exceptionPolicies>
<add name="myPolicy">
<exceptionTypes>
<add name="InvalidUserNameException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
<add name="UserNamePasswordNotMatchException" type="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
postHandlingAction="ThrowNewException">
...
</add>
</exceptionTypes>
</add>
</exceptionPolicies>
</exceptionHandling>按照我們上面的異常處理策略,在這種情況下我們將采用“錯(cuò)誤頁(yè)面”的方式來(lái)進(jìn)行異常處理。也HandleErrorAttribute的處理方式類似,我們支持異常類型和Error View之間的匹配關(guān)系,而這是通過(guò)類似于如下的配置來(lái)定義的。值得一提的是,這里的異常類型是經(jīng)過(guò)處理后重新拋出的異常。
<artech.exceptionHandling>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.InvalidUserNameException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="InvalideUserNameError"/>
<add exceptionType="Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Models.UserNamePasswordNotMatchException, Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling"
errorView="UserNamePasswordNotMatchError"/>
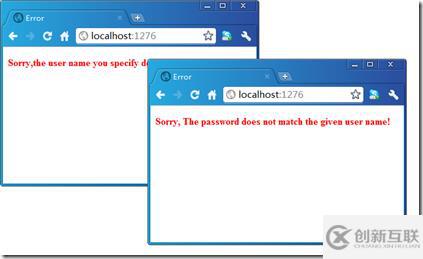
</artech.exceptionHandling>如上面的配置所示,我們?yōu)镮nvalidUserNameException和UserNamePasswordNotMatchException這兩種異常類型定義了不同的Error View,分別是“InvalideUserNameError”和“UserNamePasswordNotMatchError”,詳細(xì)定義如下所示:
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry,the user name you specify does not exist!</p>
</body>
</html>
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<p style="colorRed; font-weightbold">Sorry, The password does not match the given user name!</p>
</body>
</html>現(xiàn)在我們按照上面的方式運(yùn)行我們的程序,在分別輸入錯(cuò)誤的用戶名和密碼的情況下會(huì)自動(dòng)顯現(xiàn)相應(yīng)的錯(cuò)誤頁(yè)面。
四、自定義ActionInvoker:ExceptionActionInvoker
對(duì)于上述的兩種不同的異常處理方式最終是通過(guò)自定義的ActionInvoker來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的,我們將其命名為ExceptionActionInvoker。如下面的代碼片斷所式,ExceptionActionInvoker直接繼承自ControllerActionInvoker。屬性ExceptionPolicy是一個(gè)基于指定的異常策略名稱創(chuàng)建的ExceptionPolicyImpl 對(duì)象,用于針對(duì)EntLib進(jìn)行的異常處理。而屬性GetErrorView是一個(gè)用于獲得作為錯(cuò)誤頁(yè)面的ViewResult對(duì)象的委托。整個(gè)異常處理的核心定義在InvokeAction方法中,該方法中指定的handleErrorActionName參數(shù)代表的是“異常處理操作名稱”,整個(gè)方法就是按照上述的異常處理策略實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.Common.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Practices.EnterpriseLibrary.ExceptionHandling;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public class ExceptionActionInvoker ControllerActionInvoker
{
protected ExceptionHandlingSettings ExceptionHandlingSettings{get; private set;}
protected virtual Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> GetErrorView { get; private set; }
public ExceptionPolicyImpl ExceptionPolicy { get; private set; }
public ExceptionActionInvoker(string exceptionPolicy,Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView)
{
this.ExceptionPolicy = EnterpriseLibraryContainer.Current.GetInstance<ExceptionPolicyImpl>(exceptionPolicy);
this.GetErrorView = getErrorView;
this.ExceptionHandlingSettings = ExceptionHandlingSettings.GetSection();
}
public override bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext, string handleErrorActionName)
{
ExceptionContext exceptionContext = controllerContext as ExceptionContext;
if (null == exceptionContext)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The controllerContext must be ExceptionContext!", "controllerContext");
}
try
{
exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled = true;
if (this.ExceptionPolicy.HandleException(exceptionContext.Exception))
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
else
{
if (ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Count == 0)
{
ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors.Add(exceptionContext.Exception.Message);
}
ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = this.GetControllerDescriptor(exceptionContext);
ActionDescriptor handleErrorAction = FindAction(exceptionContext, controllerDescriptor, handleErrorActionName);
if (null != handleErrorAction)
{
IDictionary<string, object> parameters = GetParameterValues(controllerContext, handleErrorAction);
exceptionContext.Result = this.InvokeActionMethod(exceptionContext, handleErrorAction, parameters);
}
else
{
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
}
}
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
exceptionContext.Exception = ex;
HandleRethrownException(exceptionContext);
return true;
}
}
protected virtual void HandleRethrownException(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
string errorViewName = this.GetErrorViewName(exceptionContext.Exception.GetType());
string controllerName = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
string action = (string)exceptionContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
HandleErrorInfo handleErrorInfo = new HandleErrorInfo(exceptionContext.Exception, controllerName, action);
exceptionContext.Result = this.GetErrorView(errorViewName, handleErrorInfo);
}
protected string GetErrorViewName(Type exceptionType)
{
ExceptionErrorViewElement element = ExceptionHandlingSettings.ExceptionErrorViews
.Cast<ExceptionErrorViewElement>().FirstOrDefault(el=>el.ExceptionType == exceptionType);
if(null != element)
{
return element.ErrorView;
}
if(null== element && null != exceptionType.BaseType!= null)
{
return GetErrorViewName(exceptionType.BaseType);
}
else
{
return "Error";
}
}
}
}五、自定義Controller:BaseController
ExceptionActionInvoker最終在我們自定義的Controller基類BaseController中被調(diào)用的。ExceptionActionInvoker對(duì)象在構(gòu)造函數(shù)中被初始化,并在重寫的OnException方法中被調(diào)用。
using System;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace Artech.Mvc.ExceptionHandling
{
public abstract class BaseController Controller
{
public BaseController(string exceptionPolicy)
{
Func<string, HandleErrorInfo, ViewResult> getErrorView = (viewName, handleErrorInfo) => this.View(viewName, handleErrorInfo);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = new ExceptionActionInvoker(exceptionPolicy,getErrorView);
}
public BaseController(ExceptionActionInvoker actionInvoker)
{
this.ExceptionActionInvoker = actionInvoker;
}
public virtual ExceptionActionInvoker ExceptionActionInvoker { get; private set; }
protected virtual string GetHandleErrorActionName(string actionName)
{
return string.Format("On{0}Error", actionName);
}
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext)
{
using (ExceptionHandlingContextScope contextScope = new ExceptionHandlingContextScope(filterContext))
{
string actionName = RouteData.GetRequiredString("action");
string handleErrorActionName = this.GetHandleErrorActionName(actionName);
this.ExceptionActionInvoker.InvokeAction(filterContext, handleErrorActionName);
foreach (var error in ExceptionHandlingContext.Current.Errors)
{
ModelState.AddModelError(Guid.NewGuid().ToString() ,error.ErrorMessage);
}
}
}
}
}值得一提的是:整個(gè)OnException方法中的操作都在一個(gè)ExceptionHandlingContextScope中進(jìn)行的。顧名思義, 我們通過(guò)ExceptionHandlingContextScope為ExceptionHandlingContext創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)范圍。ExceptionHandlingContext定義如下,我們可以通過(guò)它獲得當(dāng)前的ExceptionContext和ModelErrorCollection,而靜態(tài)屬性Current返回當(dāng)前的ExceptionHandlingContext對(duì)象。
public class ExceptionHandlingContext
{
[ThreadStatic]
private static ExceptionHandlingContext current;
public ExceptionContext ExceptionContext { get; private set; }
public ModelErrorCollection Errors { get; private set; }
public ExceptionHandlingContext(ExceptionContext exceptionContext)
{
this.ExceptionContext = exceptionContext;
this.Errors = new ModelErrorCollection();
}
public static ExceptionHandlingContext Current
{
get { return current; }
set { current = value; }
}
}在BaseController的OnException方法中,當(dāng)執(zhí)行了ExceptionActionInvoker的InvokeAction之后,我們會(huì)將當(dāng)前ExceptionHandlingContext的ModelError轉(zhuǎn)移到當(dāng)前的ModelState中。這就是為什么我們會(huì)通過(guò)ValidationSummary顯示錯(cuò)誤信息的原因。對(duì)于我們的例子來(lái)說(shuō),錯(cuò)誤消息的指定是通過(guò)如下所示的ErrorMessageSettingHandler 實(shí)現(xiàn)的,而它僅僅將指定的錯(cuò)誤消息添加到當(dāng)前ExceptionHandlingContext的Errors屬性集合中而已。
[ConfigurationElementType(typeof(ErrorMessageSettingHandlerData))]
public class ErrorMessageSettingHandler IExceptionHandler
{
public string ErrorMessage { get; private set; }
public ErrorMessageSettingHandler(string errorMessage)
{
thisErrorMessage = errorMessage;
}
public Exception HandleException(Exception exception, Guid handlingInstanceId)
{
if (null == ExceptionHandlingContextCurrent)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("");
}
if (stringIsNullOrEmpty(thisErrorMessage))
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(exceptionMessage);
}
else
{
ExceptionHandlingContextCurrentErrorsAdd(thisErrorMessage);
}
return exception;
}
}以上就是ASP.NET中EntLib出現(xiàn)異常的處理方法的簡(jiǎn)略介紹,當(dāng)然詳細(xì)使用上面的不同還得要大家自己使用過(guò)才領(lǐng)會(huì)。如果想了解更多,歡迎關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道哦!
網(wǎng)站名稱:ASP.NET中EntLib出現(xiàn)異常的處理方法
當(dāng)前URL:http://www.chinadenli.net/article44/iigshe.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供商城網(wǎng)站、微信公眾號(hào)、標(biāo)簽優(yōu)化、建站公司、全網(wǎng)營(yíng)銷推廣、網(wǎng)站建設(shè)
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 廣州市民可通過(guò)微信小程序查詢不動(dòng)產(chǎn)登記資料 2022-05-24
- 微信小程序商城如何運(yùn)營(yíng) 2021-01-31
- 微信小程序已經(jīng)普及了 2021-02-03
- 微信小程序這么火,要如何推廣小程序? 2021-02-15
- 微信小程序時(shí)代,超級(jí)流量入口 2021-02-11
- 微信小程序正式上線!扒一扒小程序到底是什么鬼 2021-02-24
- 電商微信小程序上線后,如何推廣運(yùn)營(yíng)? 2022-07-08
- 微信小程序開發(fā)教程 2020-11-13
- 微信小程序怎么玩,入口在哪里? 2022-01-30
- 微信小程序如何避免被封? 2022-09-13
- 微信小程序開發(fā)的準(zhǔn)備工作有哪些 2023-03-26
- 微信小程序有哪些特點(diǎn)? 2022-11-06