python實(shí)現(xiàn)canopy聚類(lèi)的方法
這篇文章將為大家詳細(xì)講解有關(guān)python實(shí)現(xiàn)canopy聚類(lèi)的方法,小編覺(jué)得挺實(shí)用的,因此分享給大家做個(gè)參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)建站是一家專(zhuān)業(yè)提供阿壩州企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè),專(zhuān)注與成都網(wǎng)站制作、做網(wǎng)站、外貿(mào)營(yíng)銷(xiāo)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、H5高端網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、小程序制作等業(yè)務(wù)。10年已為阿壩州眾多企業(yè)、政府機(jī)構(gòu)等服務(wù)。創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)專(zhuān)業(yè)網(wǎng)站設(shè)計(jì)公司優(yōu)惠進(jìn)行中。
Canopy算法是2000年由Andrew McCallum, Kamal Nigam and Lyle Ungar提出來(lái)的,它是對(duì)k-means聚類(lèi)算法和層次聚類(lèi)算法的預(yù)處理。眾所周知,kmeans的一個(gè)不足之處在于k值需要通過(guò)人為的進(jìn)行調(diào)整,后期可以通過(guò)肘部法則(Elbow Method)和輪廓系數(shù)(Silhouette Coefficient)來(lái)對(duì)k值進(jìn)行最終的確定,但是這些方法都是屬于“事后”判斷的,而Canopy算法的作用就在于它是通過(guò)事先粗聚類(lèi)的方式,為k-means算法確定初始聚類(lèi)中心個(gè)數(shù)和聚類(lèi)中心點(diǎn)。
使用的包:
import math import random import numpy as np from datetime import datetime from pprint import pprint as p import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
1.首先我在算法中預(yù)設(shè)了一個(gè)二維(為了方便后期畫(huà)圖呈現(xiàn)在二維平面上)數(shù)據(jù)dataset。
當(dāng)然也可以使用高緯度的數(shù)據(jù),并且我將canopy核心算法寫(xiě)入了類(lèi)中,后期可以通過(guò)直接調(diào)用的方式對(duì)任何維度的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行處理,當(dāng)然只是小批量的,大批量的數(shù)據(jù)可以移步Mahout和Hadoop了。
# 隨機(jī)生成500個(gè)二維[0,1)平面點(diǎn) dataset = np.random.rand(500, 2)
2.然后生成個(gè)兩類(lèi),類(lèi)的屬性如下:
class Canopy:
def __init__(self, dataset):
self.dataset = dataset
self.t1 = 0
self.t2 = 0加入設(shè)定t1和t2初始值以及判斷大小函數(shù)
# 設(shè)置初始閾值
def setThreshold(self, t1, t2):
if t1 > t2:
self.t1 = t1
self.t2 = t2
else:
print('t1 needs to be larger than t2!')3.距離計(jì)算,各個(gè)中心點(diǎn)之間的距離計(jì)算方法我使用的歐式距離。
#使用歐式距離進(jìn)行距離的計(jì)算
def euclideanDistance(self, vec1, vec2):
return math.sqrt(((vec1 - vec2)**2).sum())4.再寫(xiě)個(gè)從dataset中根據(jù)dataset的長(zhǎng)度隨機(jī)選擇下標(biāo)的函數(shù)
# 根據(jù)當(dāng)前dataset的長(zhǎng)度隨機(jī)選擇一個(gè)下標(biāo)
def getRandIndex(self):
return random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1)5.核心算法
def clustering(self):
if self.t1 == 0:
print('Please set the threshold.')
else:
canopies = [] # 用于存放最終歸類(lèi)結(jié)果
while len(self.dataset) != 0:
rand_index = self.getRandIndex()
current_center = self.dataset[rand_index] # 隨機(jī)獲取一個(gè)中心點(diǎn),定為P點(diǎn)
current_center_list = [] # 初始化P點(diǎn)的canopy類(lèi)容器
delete_list = [] # 初始化P點(diǎn)的刪除容器
self.dataset = np.delete(
self.dataset, rand_index, 0) # 刪除隨機(jī)選擇的中心點(diǎn)P
for datum_j in range(len(self.dataset)):
datum = self.dataset[datum_j]
distance = self.euclideanDistance(
current_center, datum) # 計(jì)算選取的中心點(diǎn)P到每個(gè)點(diǎn)之間的距離
if distance < self.t1:
# 若距離小于t1,則將點(diǎn)歸入P點(diǎn)的canopy類(lèi)
current_center_list.append(datum)
if distance < self.t2:
delete_list.append(datum_j) # 若小于t2則歸入刪除容器
# 根據(jù)刪除容器的下標(biāo),將元素從數(shù)據(jù)集中刪除
self.dataset = np.delete(self.dataset, delete_list, 0)
canopies.append((current_center, current_center_list))
return canopies為了方便后面的數(shù)據(jù)可視化,我這里的canopies定義的是一個(gè)數(shù)組,當(dāng)然也可以使用dict。
6.main()函數(shù)
def main():
t1 = 0.6
t2 = 0.4
gc = Canopy(dataset)
gc.setThreshold(t1, t2)
canopies = gc.clustering()
print('Get %s initial centers.' % len(canopies))
#showCanopy(canopies, dataset, t1, t2)Canopy聚類(lèi)可視化代碼
def showCanopy(canopies, dataset, t1, t2):
fig = plt.figure()
sc = fig.add_subplot(111)
colors = ['brown', 'green', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'tan', 'dodgerblue', 'deeppink', 'orangered', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'gold', 'dimgray', 'darkorange', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'cyan', 'tan', 'orchid', 'peru', 'blue', 'y', 'r', 'sienna']
markers = ['*', 'h', 'H', '+', 'o', '1', '2', '3', ',', 'v', 'H', '+', '1', '2', '^', '<', '>', '.', '4', 'H', '+', '1', '2', 's', 'p', 'x', 'D', 'd', '|', '_'] for i in range(len(canopies)):
canopy = canopies[i]
center = canopy[0]
components = canopy[1]
sc.plot(center[0], center[1], marker=markers[i],
color=colors[i], markersize=10)
t1_circle = plt.Circle(
xy=(center[0], center[1]), radius=t1, color='dodgerblue', fill=False)
t2_circle = plt.Circle(
xy=(center[0], center[1]), radius=t2, color='skyblue', alpha=0.2)
sc.add_artist(t1_circle)
sc.add_artist(t2_circle) for component in components:
sc.plot(component[0], component[1],
marker=markers[i], color=colors[i], markersize=1.5)
maxvalue = np.amax(dataset)
minvalue = np.amin(dataset)
plt.xlim(minvalue - t1, maxvalue + t1)
plt.ylim(minvalue - t1, maxvalue + t1)
plt.show()效果圖如下:
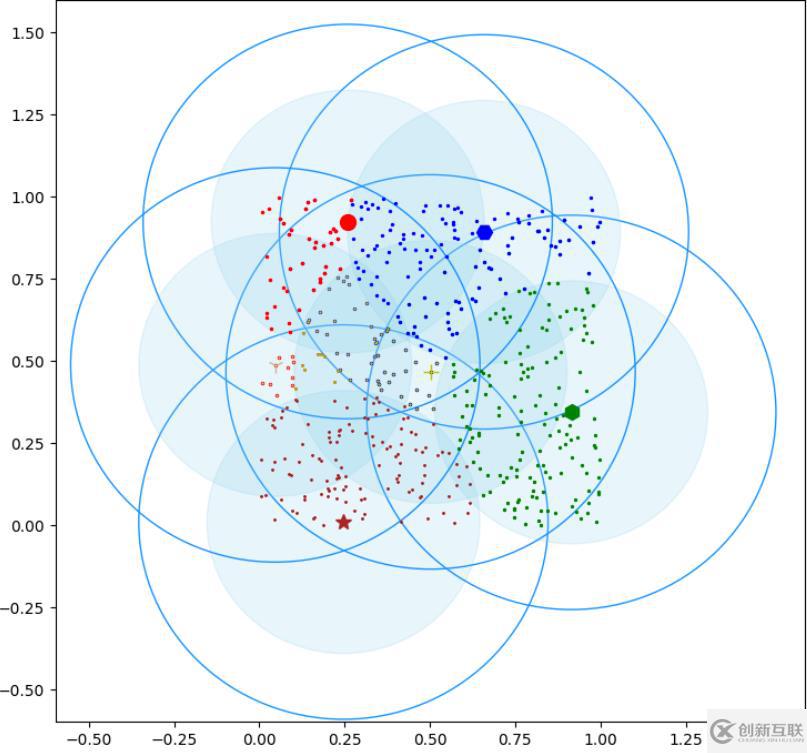
關(guān)于python實(shí)現(xiàn)canopy聚類(lèi)的方法就分享到這里了,希望以上內(nèi)容可以對(duì)大家有一定的幫助,可以學(xué)到更多知識(shí)。如果覺(jué)得文章不錯(cuò),可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
新聞名稱(chēng):python實(shí)現(xiàn)canopy聚類(lèi)的方法
當(dāng)前地址:http://www.chinadenli.net/article42/jigoec.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供網(wǎng)站營(yíng)銷(xiāo)、手機(jī)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站、靜態(tài)網(wǎng)站、搜索引擎優(yōu)化、網(wǎng)站內(nèi)鏈
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶(hù)投稿、用戶(hù)轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀(guān)點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話(huà):028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)套路太深,一不小心就會(huì)踩坑,不信你試試! 2022-05-20
- 關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化的方法有哪些? 2023-04-10
- 那些過(guò)時(shí)的關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化技巧 2020-08-27
- 鹽城網(wǎng)站優(yōu)化公司告訴你熱門(mén)行業(yè)關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化是怎么做的 2020-02-08
- 注意了!首頁(yè)核心關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化不要超過(guò)5個(gè) 2021-04-27
- 北京網(wǎng)站建設(shè)SEO關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化的7大優(yōu)點(diǎn) 2021-04-12
- 關(guān)于關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化與整站優(yōu)化的區(qū)別介紹 2023-04-07
- 單頁(yè)面網(wǎng)站關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化的潛力 2015-07-14
- 北京網(wǎng)站改版要特別注重關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化 2020-12-19
- 互聯(lián)網(wǎng)關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化合理布局怎么做? 2014-06-15
- 成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)整站優(yōu)化和關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化有什么不一樣? 2016-10-02
- 企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè)seo關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化怎么做? 2022-11-01