非比較排序-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
計數(shù)排序
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)公司專注于企業(yè)成都全網(wǎng)營銷、網(wǎng)站重做改版、烏海海南網(wǎng)站定制設計、自適應品牌網(wǎng)站建設、成都h5網(wǎng)站建設、商城建設、集團公司官網(wǎng)建設、外貿(mào)營銷網(wǎng)站建設、高端網(wǎng)站制作、響應式網(wǎng)頁設計等建站業(yè)務,價格優(yōu)惠性價比高,為烏海海南等各大城市提供網(wǎng)站開發(fā)制作服務。
計數(shù)排序算法不是一個基于比較的排序算法,而且一種穩(wěn)定的排序算法。
計數(shù)排序該算法于1954年由 Harold H. Seward 提出。它的優(yōu)勢在于在對一定范圍內的整數(shù)排序時,它的復雜度為Ο(n+k)(其中k是整數(shù)的范圍),快于任何比較排序算法。
計數(shù)排序的基本思想是對于給定的輸入序列中的每一個元素x,確定該序列中值小于x的元素的個數(shù)(此處并非比較各元素的大小,而是通過對元素值的計數(shù)和計數(shù)值的累加來確定)。一旦有了這個信息,就可以將x直接存放到最終的輸出序列的正確位置上。例如,如果輸入序列中只有17個元素的值小于x的值,則x可以直接存放在輸出序列的第18個位置上。當然,如果有多個元素具有相同的值時,我們不能將這些元素放在輸出序列的同一個位置上,因此,上述方案還要作適當?shù)男薷摹?/p>
代碼實現(xiàn):
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
//計數(shù)排序
//
//選取大的數(shù),選取最小的數(shù),開辟Max-Min+1個空間
void GetMinMax(int *a, int size, int *max, int *min)
{
assert(a);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (a[i] < *min)
{
*min = a[i];
}
if (a[i]>*max)
{
*max = a[i];
}
}
return;
}
void CountSort(int *a, int size)
{
assert(a);
int max = a[0];
int min = a[0];
GetMinMax(a, size, &max, &min);
int newsize = max - min + 1;
int *count=new int[newsize];
memset(count, 0, (sizeof(int))*newsize);
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
(count[a[j] - min])++;
}
int index = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < newsize; k++)
{
int number = count[k];
while (number>0)
{
a[index++] = k + min;
number--;
}
}
delete[]count;
return;
}測試案例:
void CountSortTest()
{
int array1[] = { 12, 5, 18, 19, 0, 5, 7, 3, 6 };
CountSort(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
Print(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
int array2[] = { 12, 5, 3,18, 3,19, 0, 5,3, 7, 3, 6 };
CountSort(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
Print(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
return;
}基數(shù)排序
(radixsort)則是屬于“分配式排序”(distributionsort),基數(shù)排序法又稱“桶子法”(bucketsort)或binsort,顧名思義,它是透過鍵值的部份資訊,將要排序的元素分配至某些“桶”中,藉以達到排序的作用,基數(shù)排序法是屬于穩(wěn)定性的排序,其時間復雜度為O(nlog(r)m),其中r為所采取的基數(shù),而m為堆數(shù),在某些時候,基數(shù)排序法的效率高于其它的比較性排序法。基數(shù)排序的發(fā)明可以追溯到1887年赫爾曼·何樂禮在打孔卡片制表機(Tabulation Machine)上的貢獻。
以MLD為例,如圖:
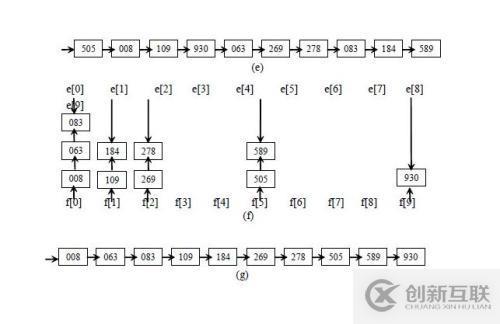
代碼實現(xiàn):
//基數(shù)排序
//得到數(shù)據(jù)的大位數(shù)
int GetMaxRadix(int *a, size_t size)
{
int radix = 1;
int max = 10;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
while (a[i]>max)
{
radix += 1;
max *= 10;
}
}
return radix;
}
//得到數(shù)據(jù)某一位數(shù)
int Data_k_Bit(int data,int k)
{
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++)
{
data /= 10;
}
return data % 10;
}
//從低位到高位排序
void LSDSort(int a[], size_t size)
{
assert(a);
int maxRadix = GetMaxRadix(a, size);
int count[10] = { 0 };//存放尾數(shù)為0-9的個數(shù)
int start[10] = { 0 };//開始存放數(shù)據(jù)的位置
int *bucket = new int[size];
//計數(shù)個位分別為0—9的個數(shù)
for (int i = 1; i <= maxRadix; ++i)
{
memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; ++j)
{
int num = Data_k_Bit(a[j], i);
count[num]++;
}
start[0] = 0;
size_t index = 1;
for (; index < 10; index++)
{
start[index] = start[index - 1] + count[index - 1];
}
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; ++j)
{
int num = Data_k_Bit(a[j], i);
bucket[start[num]++] = a[j];
}
memcpy(a, bucket, sizeof(int)*size);
}
delete[]bucket;
}
void Print(int *a, int size)
{
assert(a);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
void MSDSort(int *a, size_t size)
{
int count[10] = {0};
int start[10] = {0};
int *bucket = new int[size];
int maxRadix = GetMaxRadix(a, size);
for (int i = maxRadix; i >= 1; i--)
{
memset(count, 0, sizeof(count));
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
int num = Data_k_Bit(a[j], i);
count[num]++;
}
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++)
{
start[j] = start[j - 1] + count[j - 1];
}
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
int num = Data_k_Bit(a[j], i);
bucket[start[num]++] = a[j];
}
memcpy(a, bucket, sizeof(int)*size);
}
delete[]bucket;
//delete[]bucket;
}測試案例:
void LSDSorTest()
{
int array1[] = { 12, 5, 18, 19, 0, 5, 7, 3, 6 };
LSDSort(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
Print(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
int array2[] = { 12, 5, 3, 18, 3, 19, 0, 5, 3, 7, 3, 6 };
LSDSort(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
Print(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
return;
}
void MSDSorTest()
{
int array1[] = { 12, 5, 18, 19, 0, 5, 7, 3, 6 };
MSDSort(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
Print(array1, sizeof(array1) / sizeof(int));
int array2[] = { 12, 5, 3, 18, 3, 19, 0, 5, 3, 7, 3, 6 };
MSDSort(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
Print(array2, sizeof(array2) / sizeof(int));
return;
}另外有需要云服務器可以了解下創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)scvps.cn,海內外云服務器15元起步,三天無理由+7*72小時售后在線,公司持有idc許可證,提供“云服務器、裸金屬服務器、高防服務器、香港服務器、美國服務器、虛擬主機、免備案服務器”等云主機租用服務以及企業(yè)上云的綜合解決方案,具有“安全穩(wěn)定、簡單易用、服務可用性高、性價比高”等特點與優(yōu)勢,專為企業(yè)上云打造定制,能夠滿足用戶豐富、多元化的應用場景需求。
名稱欄目:非比較排序-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
網(wǎng)站地址:http://www.chinadenli.net/article42/ccseec.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供Google、企業(yè)建站、網(wǎng)頁設計公司、標簽優(yōu)化、網(wǎng)站收錄、ChatGPT
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內容未經(jīng)允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 北京朝陽app開發(fā)公司 2022-05-04
- 手機物聯(lián)網(wǎng)app開發(fā) 2022-11-07
- 上海app開發(fā)報價 2020-12-29
- 青島園林APP開發(fā)的必要性和功能分析 2023-02-15
- 淺析成都app開發(fā)對集團的意義 2022-07-30
- 成都網(wǎng)站建設:小程序開發(fā)與APP開發(fā),企業(yè)究竟應該如何選擇? 2017-01-07
- 上海智能灌溉APP開發(fā)對用戶有哪些價值 2020-12-29
- 寵物社交APP開發(fā)市場現(xiàn)狀分析 2022-06-21
- 個性化APP開發(fā)對企業(yè)有什么好處 2021-05-25
- 成都商城APP開發(fā)多少錢? 2022-06-26
- APP開發(fā)公司與您分享定制app要了解的知識 2020-11-21
- 手機APP開發(fā)的幾種叫法,按手機系統(tǒng)區(qū)分手機APP,按開發(fā)方式區(qū)分手機APP。 2021-06-03