怎么在python中實現(xiàn)SVM線性分類模型-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
怎么在python中實現(xiàn)SVM 線性分類模型?很多新手對此不是很清楚,為了幫助大家解決這個難題,下面小編將為大家詳細講解,有這方面需求的人可以來學習下,希望你能有所收獲。

導入對應(yīng)的包和數(shù)據(jù)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn import datasets,linear_model,cross_validation,svm def load_data_regression(): diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes() return cross_validation.train_test_split(diabetes,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) def load_data_classfication(): iris = datasets.load_iris() X_train = iris.data y_train = iris.target return cross_validation.train_test_split(X_train,y_train,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y_train)
#線性分類SVM
def test_LinearSVC(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
cls = svm.LinearSVC()
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)def test_LinearSVC_loss(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
losses = ['hinge','squared_hinge']
for loss in losses:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(loss=loss)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('loss:%s'%loss)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)#考察罰項形式的影響
def test_LinearSVC_L12(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
L12 = ['l1','l2']
for p in L12:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(penalty=p,dual=False)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('penalty:%s'%p)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_L12(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)#考察罰項系數(shù)C的影響
def test_LinearSVC_C(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = data
Cs = np.logspace(-2,1)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for C in Cs:
cls = svm.LinearSVC(C=C)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test,y_test))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(Cs,train_scores,label = 'Training score')
ax.plot(Cs,test_scores,label = 'Testing score')
ax.set_xlabel(r'C')
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_title('LinearSVC')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_LinearSVC_C(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)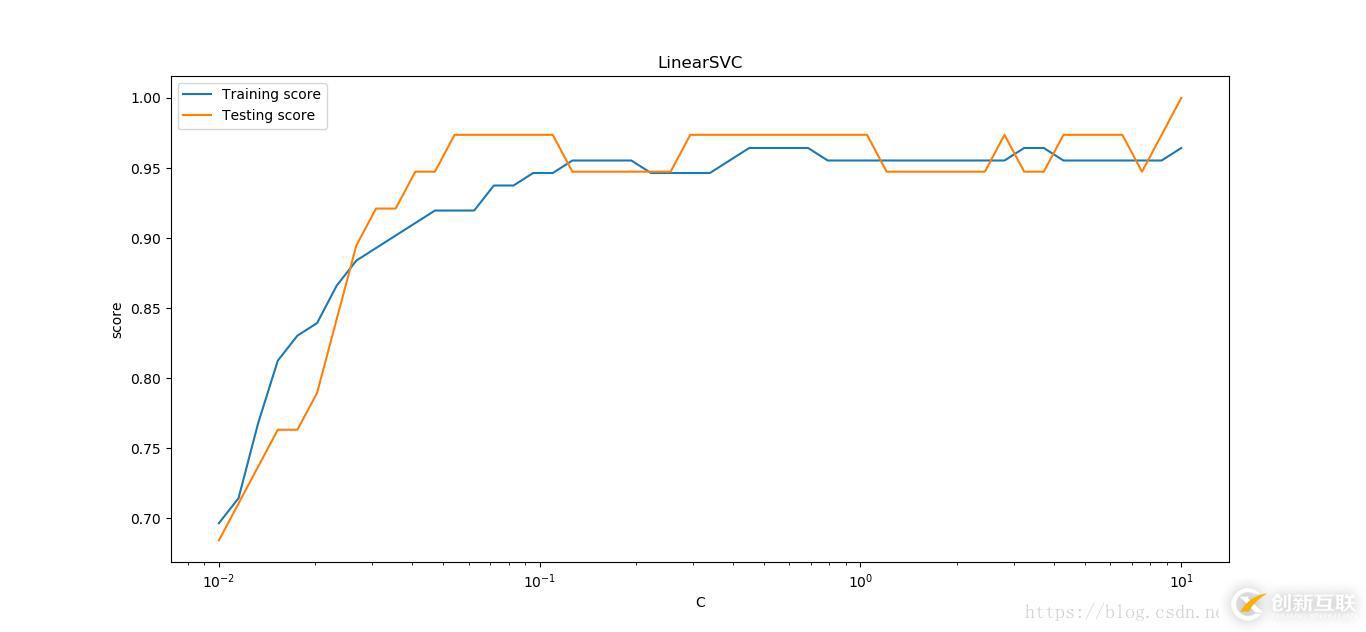
#非線性分類SVM
#線性核
def test_SVC_linear(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Coefficients:%s,intercept%s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score:%.2f'%cls.score(X_test,y_test))
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_linear(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)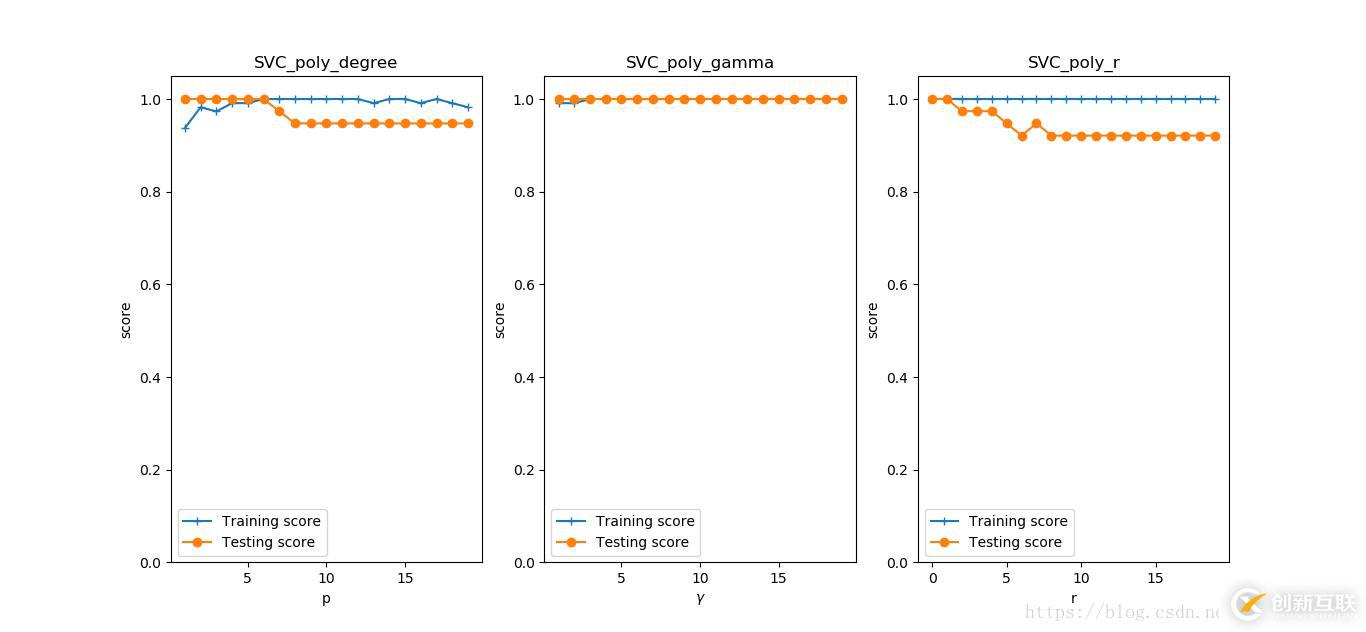
#考察高斯核
def test_SVC_rbf(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
###測試gamm###
gamms = range(1, 20)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for gamm in gamms:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf', gamma=gamm)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(gamms, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(gamms, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\gamma$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_rbf')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_rbf(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)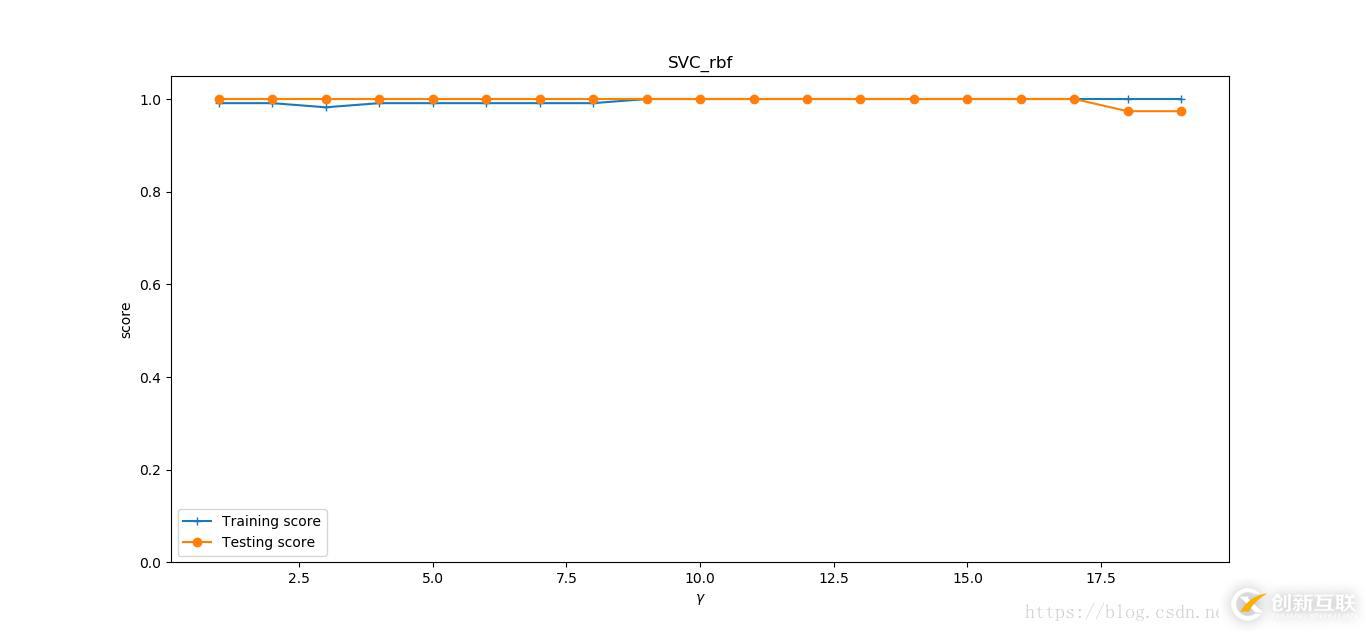
#考察sigmoid核
def test_SVC_sigmod(*data):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = data
fig = plt.figure()
###測試gamm###
gamms = np.logspace(-2, 1)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for gamm in gamms:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid',gamma=gamm,coef0=0)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax.plot(gamms, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(gamms, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\gamma$')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_sigmoid_gamm')
ax.legend(loc='best')
#測試r
rs = np.linspace(0,5)
train_scores = []
test_scores = []
for r in rs:
cls = svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid', gamma=0.01, coef0=r)
cls.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train, y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax.plot(rs, train_scores, label='Training score', marker='+')
ax.plot(rs, test_scores, label='Testing score', marker='o')
ax.set_xlabel(r'r')
ax.set_ylabel(r'score')
ax.set_ylim(0, 1.05)
ax.set_title('SVC_sigmoid_r')
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = load_data_classfication()
test_SVC_sigmod(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)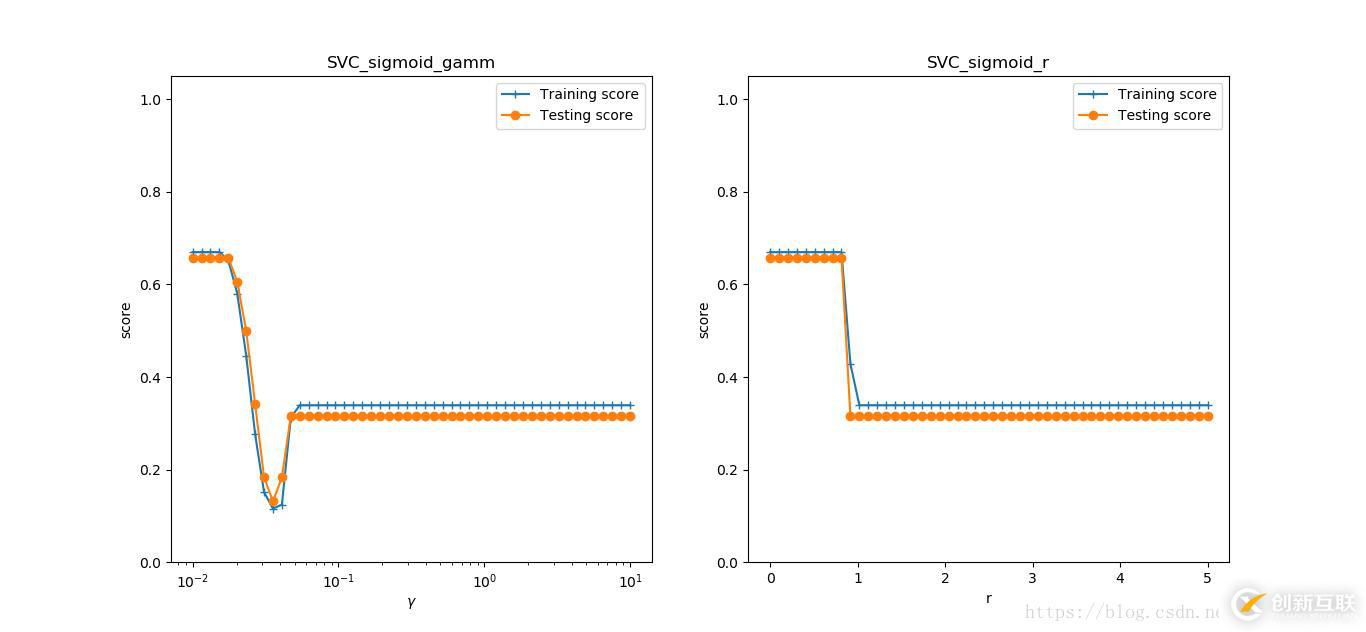
看完上述內(nèi)容是否對您有幫助呢?如果還想對相關(guān)知識有進一步的了解或閱讀更多相關(guān)文章,請關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道,感謝您對創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)的支持。
本文名稱:怎么在python中實現(xiàn)SVM線性分類模型-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
網(wǎng)頁路徑:http://www.chinadenli.net/article4/dodjie.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供企業(yè)網(wǎng)站制作、商城網(wǎng)站、動態(tài)網(wǎng)站、響應(yīng)式網(wǎng)站、面包屑導航、網(wǎng)頁設(shè)計公司
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
猜你還喜歡下面的內(nèi)容

- 小程序開發(fā)的費用和什么因素有關(guān)? 2014-04-26
- 律師微信小程序開發(fā)感想 2023-02-26
- 商家開發(fā)小程序的步驟是什么? 2014-03-04
- 自建外賣小程序開發(fā)與入駐外賣平臺該怎么選? 2021-01-06
- 微信小程序開發(fā)的必要性 2021-01-30
- 如何選擇一個正規(guī)的小程序開發(fā)公司? 2021-09-24
- 上海智能健康穿戴小程序開發(fā)有哪些優(yōu)勢 2021-01-04
- 小程序排名靠前的方法 2017-05-05
- 小程序和HTML5它們之間的區(qū)別 2016-10-13
- 北京微信小程序開發(fā)公司哪家好? 2022-07-17
- 如何在微信公眾號關(guān)聯(lián)小程序的呢? 2015-05-31
- 小程序開發(fā)需要用到哪些技術(shù)? 2022-08-21