Android如何自定義StepView仿外賣配送進度-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
小編給大家分享一下Android如何自定義StepView仿外賣配送進度,相信大部分人都還不怎么了解,因此分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后大有收獲,下面讓我們一起去了解一下吧!

效果圖
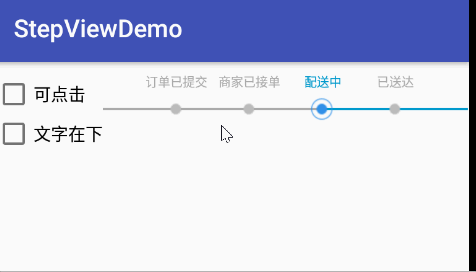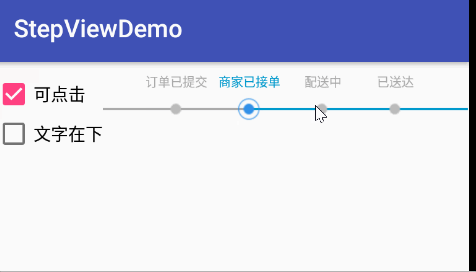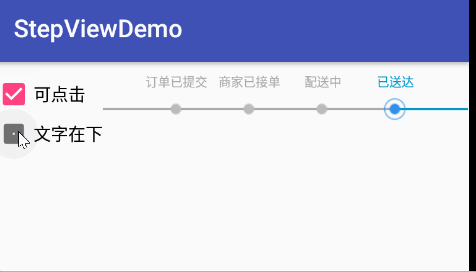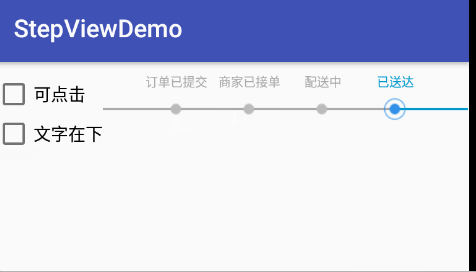
使用
可在layout文件下設置以下屬性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="StepView"> <attr name="step_size" format="dimension"/><!--step的size,也就是image的大小--> <attr name="line_size" format="dimension"/><!--線寬--> <attr name="text_size" format="dimension"/><!--文字大小--> <attr name="text_line_margin" format="dimension"/><!--文字和線之間的間距--> <attr name="normal_line_color" format="color"/><!--一般線的顏色--> <attr name="normal_text_color" format="color"/><!--一般文字的顏色--> <attr name="target_text_color" format="color"/><!--一般文字的顏色--> <attr name="passed_line_color" format="color"/><!--已經(jīng)過線的顏色--> <attr name="step_count" format="integer"/><!--總step數(shù)--> <attr name="current_step" format="integer"/><!--當前step位置--> <attr name="normal_step_iv" format="reference"/><!--一般圖片--> <attr name="passed_step_iv" format="reference"/><!--已經(jīng)過的圖片--> <attr name="target_step_iv" format="reference"/><!--當前step圖片--> <attr name="step_is_touch" format="boolean"/><!--step是否可點--> <attr name="text_up_line" format="boolean"/><!--文字是否在線上--> </declare-styleable> </resources>
CheckBox cbTouch = findViewById(R.id.cb_touch);
CheckBox cbIsDown = findViewById(R.id.cb_is_down);
final StepView stepView = findViewById(R.id.step_view);
String[] stepTexts = new String[]{"訂單已提交", "商家已接單", "配送中", "已送達"};
stepView.setStepTexts(stepTexts);//傳入每一進度的文字描述
stepView.setCurrentStep(2);//設置當前進度所在位置
stepView.setOnItemStepTouchListener(new StepView.OnItemStepTouchListener() {
@Override
public void onItemStepTouch(int postion) {
Log.d(TAG, "當前點擊位置: "+postion);
}
});
cbTouch.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
stepView.setStepIsTouch(isChecked);
}
});
cbIsDown.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
stepView.setTextUpLine(!isChecked);
}
});步驟
1、在構造函數(shù)中初始化文字、線、step圖片的屬性。
public StepView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context, attrs);
}
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
mLinePaint = new Paint();
mLinePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPreLineLength = 0;
//默認的step圖片
mNormalBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_normal);
mPassedBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_passed);
mTargetBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.ic_target);
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.StepView);
//獲取xml文件中的線的顏色值、size
mNormalLineColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.StepView_normal_line_color, Color.BLUE);
mPassedLineColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.StepView_passed_line_color, Color.WHITE);
int lineSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.StepView_line_size, 2);
//獲取xml文件中的文本的顏色值、size
mNormalTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.StepView_normal_text_color, Color.BLACK);
mTargetTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.StepView_target_text_color, Color.BLACK);
int textSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.StepView_text_size, 10);
//獲取xml文件中的step的size,設置給step圖片的高度
int stepSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.StepView_step_size, 0);
//獲取xml文件中的文本和線之間的間距
mTextLineMargin = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.StepView_text_line_margin, 3);
//獲取xml文件中的step總數(shù)
mStepCount = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.StepView_step_count, 2);
//獲取xml文件中的當前step位置
mCurrentStep = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.StepView_current_step, 0);
//獲取xml文件中step圖片
BitmapDrawable normalDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) typedArray.getDrawable(R.styleable.StepView_normal_step_iv);
BitmapDrawable passedDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) typedArray.getDrawable(R.styleable.StepView_passed_step_iv);
BitmapDrawable targetDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) typedArray.getDrawable(R.styleable.StepView_target_step_iv);
//獲取xml文件中step是否可點擊TRUE可以,F(xiàn)ALSE不可以,默認為FALSE
mStepIsTouch = typedArray.getBoolean(R.styleable.StepView_step_is_touch, false);
//獲取xml文件中text是否在線上,TRUE在線上,F(xiàn)ALSE不在線上,默認為FALSE
mTextUpLine = typedArray.getBoolean(R.styleable.StepView_text_up_line, true);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(textSize);
mLinePaint.setStrokeWidth(lineSize);
mNormalBitmap = normalDrawable.getBitmap();//將xml文件中指定的圖片賦給對應的bitmap
mPassedBitmap = passedDrawable.getBitmap();
mTargetBitmap = targetDrawable.getBitmap();
mNormalBitmapWH = getBitmapWH(stepSize, mNormalBitmap);
mPassedBitmapWH = getBitmapWH(stepSize, mPassedBitmap);
mTargetBitmapWH = getBitmapWH(stepSize, mTargetBitmap);
if (stepSize != 0) {//如果stepSize不為0,要對其進行壓縮處理,使其高度等于stepSize
mNormalBitmap = zoomImg(mNormalBitmap, mNormalBitmapWH);
mPassedBitmap = zoomImg(mPassedBitmap, mPassedBitmapWH);
mTargetBitmap = zoomImg(mTargetBitmap, mPassedBitmapWH);
}
mStepRectFs = new RectF[mStepCount];//初始化step所對應的矩陣數(shù)組,點擊step時會用到,用于確定點擊的是哪個step
typedArray.recycle();
}2、在onMeasure中對StepView的寬高進行設置,并根據(jù)StepView的寬高計算每條直線的長度。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int width = widthSize - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();//任何模式下with都是父容器給定的with-padding值
int height = 0;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = heightSize - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
} else {
height = dp2px(getContext(), 80);
}
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
mPreLineLength = width / (mStepCount + 1);//計算每條線的長度,由于線比step多一個所以加1
}3、開始繪制,先畫線,再畫step和文字。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mStepCount != 0) {
drawLine(canvas);//drawLine和drawStep分兩次循環(huán)是為了防止部分線覆蓋step
drawStep(canvas);
}
}4、畫線,前一條線的stopX坐標是下一條線的startX坐標,并根據(jù)當前step所在的位置對lineColor進行設置。
private void drawLine(Canvas canvas) {
float lineStartX = getPaddingLeft();
float lineStartY = getLineStartY();
float lineStopX = 0;
float lineStopY = lineStartY;
for (int i = 0; i < mStepCount + 1; i++) {
if (i < mCurrentStep - 1) {
mLinePaint.setColor(mPassedLineColor);
} else if (i == mCurrentStep - 1) {
mLinePaint.setColor(mPassedLineColor);
} else {
mLinePaint.setColor(mNormalLineColor);
}
lineStopX = lineStartX + mPreLineLength;
canvas.drawLine(lineStartX, lineStartY, lineStopX, lineStopY, mLinePaint);
lineStartX = lineStopX;
}
}5、畫step和文字。
private void drawStep(Canvas canvas) {
float lineStartX = getPaddingLeft();
float lineStartY = getLineStartY();
Bitmap currentBitmap;
int[] currentBitmapWH;
float lineStopX;
float bitmapLeft;
float bitmapTop;
for (int i = 0; i < mStepCount; i++) {
if (i < mCurrentStep - 1) {
currentBitmap = mPassedBitmap;
currentBitmapWH = mPassedBitmapWH;
mTextPaint.setColor(mNormalTextColor);
} else if (i == mCurrentStep - 1) {
currentBitmap = mTargetBitmap;
currentBitmapWH = mTargetBitmapWH;
mTextPaint.setColor(mTargetTextColor);
} else {
currentBitmap = mNormalBitmap;
currentBitmapWH = mNormalBitmapWH;
mTextPaint.setColor(mNormalTextColor);
}
lineStopX = lineStartX + mPreLineLength;
bitmapLeft = lineStopX - currentBitmapWH[0] / 2;
bitmapTop = lineStartY - currentBitmapWH[1] / 2;
canvas.drawBitmap(currentBitmap, bitmapLeft, bitmapTop, null);
mStepRectFs[i] = new RectF(bitmapLeft, bitmapTop, bitmapLeft + currentBitmapWH[0], bitmapTop + currentBitmapWH[1]);
if (mStepTexts != null) {//當沒有傳入對應的texts時不需要劃線
drawText(canvas, i, bitmapLeft + currentBitmapWH[1] / 2, bitmapTop, currentBitmapWH[1]);//傳入step中點坐標
}
lineStartX = lineStopX;
}
}
private void drawText(Canvas canvas, int i, float x, float y, float bitmapH) {
String text = mStepTexts[i];
int[] textWH = getTextWH(text);
int textWidth = textWH[0];
int textHeight = textWH[1];
float bottom = 0;
if (mTextUpLine) {//畫文本時的基準點是left.bottom,使其中心點與step的中心點對其
bottom = y - mTextLineMargin;
} else {
bottom = y + bitmapH + mTextLineMargin + textHeight;
}
canvas.drawText(text, x - textWidth / 2, bottom, mTextPaint);
}6、對觸摸事件進行處理。
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (!mStepIsTouch) {//不能點擊返回FALSE不處理
return false;
}
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
float x = event.getX();
float y = event.getY();
int touchStep = getTouchStep(new PointF(x, y));//獲取被點擊的點的位置
if (touchStep != -1) {
mCurrentStep = touchStep + 1;
invalidate();
}
break;
}
return true;
}7、step的觸摸監(jiān)聽。
private OnItemStepTouchListener mOnItemStepTouchListener;
public void setOnItemStepTouchListener(OnItemStepTouchListener onItemStepTouchListener) {
mOnItemStepTouchListener = onItemStepTouchListener;
}
//每一個step的觸摸監(jiān)聽
public interface OnItemStepTouchListener {
void onItemStepTouch(int postion);
}8、設置當前進度所在位置,也可在layout文件中通過current_step屬性進行設置。
//設置當前step
public void setCurrentStep(int currentStep) {
mCurrentStep = currentStep;
invalidate();
}9、設置step對應的文字,不傳入不會顯示文字。
//設置step對應的texts
public void setStepTexts(String[] stepTexts) {
mStepTexts = stepTexts;
mStepCount = mStepTexts.length;
mStepRectFs = new RectF[mStepCount];//初始化step所對應的矩陣數(shù)組,點擊step時會用到,用于確定點擊的是哪個step
}10、設置step是否可點擊,不出入默認為false不可點擊,也可在layout文件中通過step_is_touch屬性進行設置。
public void setStepIsTouch(boolean stepIsTouch) {
mStepIsTouch = stepIsTouch;
}11、設置文字是否在線上,不傳入默認為true在線上,也可在layout文件中通過text_up_line屬性進行設置。
public void setTextUpLine(boolean textUpLine) {
mTextUpLine = textUpLine;
invalidate();
}以上是“Android如何自定義StepView仿外賣配送進度”這篇文章的所有內(nèi)容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內(nèi)容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道!
網(wǎng)站題目:Android如何自定義StepView仿外賣配送進度-創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)
網(wǎng)站地址:http://www.chinadenli.net/article4/decjie.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供動態(tài)網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)頁設計公司、軟件開發(fā)、面包屑導航、企業(yè)建站、網(wǎng)站建設
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權請盡快告知,我們將會在第一時間刪除。文章觀點不代表本網(wǎng)站立場,如需處理請聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉載,或轉載時需注明來源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 預訂民宿APP軟件開發(fā)具有什么好處 2022-05-31
- 選擇軟件開發(fā)公司制作APP優(yōu)勢更明顯 2022-06-29
- IT 人眼里最吃香的技術:軟件開發(fā) JavaScript;數(shù)據(jù)專業(yè) R等 2021-02-23
- 邏輯思維:軟件開發(fā)行業(yè)的發(fā)展趨勢 2016-08-02
- 軟件開發(fā)項目中如何進行風險管理 2016-08-18
- 西安音樂歌曲app軟件開發(fā) 2020-12-30
- 人工智能的發(fā)展會不會全面取代軟件開發(fā)崗位 2016-08-22
- 軟件開發(fā)者必備的軟技能有哪些? 2021-06-13
- 美容院加盟運營系統(tǒng)軟件開發(fā) 2021-05-14
- 鋼琴APP軟件開發(fā)詳細優(yōu)勢介紹 2022-06-06
- 免費的軟件開發(fā)和開源軟件能不能用 2016-08-16
- 成都兒童教育APP軟件開發(fā)如何讓孩子更主動學習? 2023-02-20