Opencv中透視變換的示例分析
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“Opencv中透視變換的示例分析”,內(nèi)容簡(jiǎn)而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領(lǐng)大家一起研究并學(xué)習(xí)一下“Opencv中透視變換的示例分析”這篇文章吧。
創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)公司是一家專業(yè)提供宜良企業(yè)網(wǎng)站建設(shè),專注與成都做網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、成都h5網(wǎng)站建設(shè)、小程序制作等業(yè)務(wù)。10年已為宜良眾多企業(yè)、政府機(jī)構(gòu)等服務(wù)。創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)專業(yè)網(wǎng)絡(luò)公司優(yōu)惠進(jìn)行中。
案例背景:對(duì)下面發(fā)生畸變的圖像進(jìn)行校正

方案思路:灰度二值化分割,閉操作,尋找輪廓,霍夫直線檢測(cè),直線排序,直線方程,直線交點(diǎn),透視矩陣,透視變換。
#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int arc, char** argv) {
Mat src = imread("1.jpg");
namedWindow("input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("input", src);
//灰度化
Mat grayImg;
cvtColor(src, grayImg, CV_BGR2GRAY);
//二值化
Mat binaryImg;
threshold(grayImg, binaryImg, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV | THRESH_OTSU);
//閉操作
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT,Size(3,3));
morphologyEx(binaryImg, binaryImg, MORPH_CLOSE,kernel,Point(-1,-1) ,3);
imshow("output", binaryImg);
//尋找輪廓
Mat draw = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
vector<vector<Point>>contours;
findContours(binaryImg, contours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) {
Rect rect = boundingRect(contours[i]);
if (rect.width < src.cols / 2 && rect.height < src.rows / 2)continue;
drawContours(draw, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
}
imshow("output2", draw);
//霍夫直線檢測(cè)
vector<Vec4i> lines;
cvtColor(draw, draw, CV_BGR2GRAY);
HoughLinesP(draw, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, src.rows/2,src.rows/2,0);
Mat draw2 = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
for (int j = 0; j < lines.size(); j++) {
Vec4i ln = lines[j];
line(draw2, Point(ln[0], ln[1]), Point(ln[2], ln[3]), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
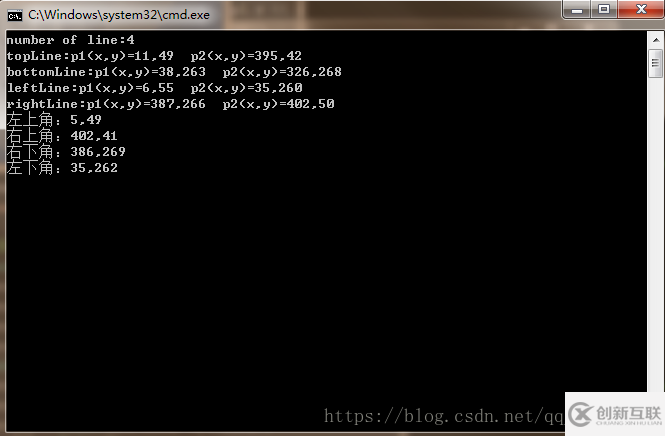
printf("number of line:%d\n", lines.size());
imshow("output3", draw2);
//尋找與定位直線
Vec4i topLine,bottomLine,leftLine,rightLine;
for (int j = 0; j < lines.size(); j++) {
Vec4i ln = lines[j];
if (ln[1] < src.rows / 2 && ln[3] < src.rows / 2) {
topLine = ln;
}
if (ln[1] > src.rows / 2 && ln[3] > src.rows / 2) {
bottomLine = ln;
}
if (ln[0] < src.cols / 2 && ln[2] < src.cols / 2) {
leftLine = ln;
}
if (ln[0] > src.cols / 2 && ln[2] > src.cols / 2) {
rightLine = ln;
}
}
cout << "topLine:p1(x,y)=" << topLine[0] << "," << topLine[1]<<" " << "p2(x,y)=" << topLine[2] << "," << topLine[3] << endl;
cout << "bottomLine:p1(x,y)=" << bottomLine[0] << "," << bottomLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << bottomLine[2] << "," << bottomLine[3] << endl;
cout << "leftLine:p1(x,y)=" << leftLine[0] << "," << leftLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << leftLine[2] << "," << leftLine[3] << endl;
cout << "rightLine:p1(x,y)=" << rightLine[0] << "," << rightLine[1] << " " << "p2(x,y)=" << rightLine[2] << "," << rightLine[3] << endl;
//求解直線方程
float k1, c1;
k1 = float((topLine[3] - topLine[1])) / float(topLine[2] - topLine[0]);
c1 = topLine[1] - k1*topLine[0];
float k2, c2;
k2 = float((bottomLine[3] - bottomLine[1])) / float(bottomLine[2] - bottomLine[0]);
c2 = bottomLine[1] - k2*bottomLine[0];
float k3, c3;
k3 = float((leftLine[3] - leftLine[1])) / float(leftLine[2] - leftLine[0]);
c3 = leftLine[1] - k3*leftLine[0];
float k4, c4;
k4 = float((rightLine[3] - rightLine[1])) / float(rightLine[2] - rightLine[0]);
c4 = rightLine[1] - k4*rightLine[0];
//求解直線交點(diǎn)
Point p1;
p1.x = (int)((c1 - c3) / (k3 - k1));
p1.y = (int)(k1*p1.x + c1);
Point p2;
p2.x = (int)((c1 - c4) / (k4 - k1));
p2.y = (int)(k1*p2.x + c1);
Point p3;
p3.x = (int)((c2 - c4) / (k4 - k2));
p3.y = (int)(k2*p3.x + c2);
Point p4;
p4.x = (int)((c2 - c3) / (k3 - k2));
p4.y = (int)(k2*p4.x + c2);
cout << "左上角:" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << endl;
cout << "右上角:" << p2.x << "," << p2.y << endl;
cout << "右下角:" << p3.x << "," << p3.y << endl;
cout << "左下角:" << p4.x << "," << p4.y << endl;
//畫(huà)出交點(diǎn)
circle(draw2, p1, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
circle(draw2, p2, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
circle(draw2, p3, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
circle(draw2, p4, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
imshow("output4", draw2);
//透視變換
vector<Point2f> srcCorners(4);
srcCorners[0] = p1;
srcCorners[1] = p2;
srcCorners[2] = p3;
srcCorners[3] = p4;
vector<Point2f> dstCorners(4);
dstCorners[0] = Point(0, 0);
dstCorners[1] = Point(src.cols, 0);
dstCorners[2] = Point(src.cols, src.rows);
dstCorners[3] = Point(0, src.rows);
Mat warpMartrix = getPerspectiveTransform(srcCorners, dstCorners);//Mat warpMartrix = findHomography(srcCorners, dstCorners);
Mat result = Mat::zeros(src.size(), -1);
warpPerspective(src, result, warpMartrix, result.size(),INTER_LINEAR);
imshow("output5", result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
原圖像
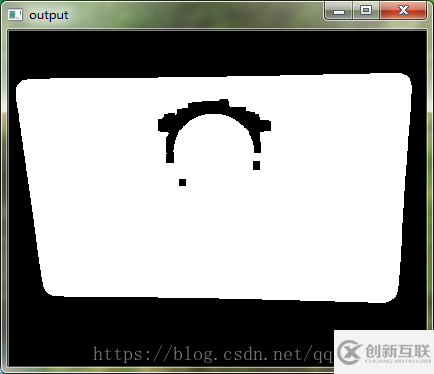
二值化閉操作
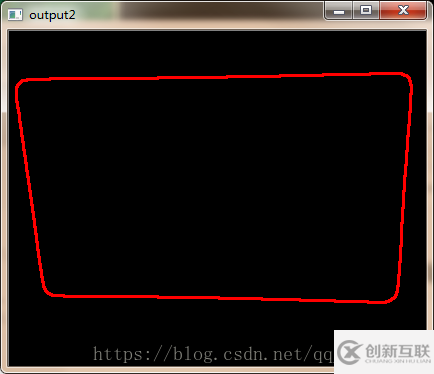
尋找輪廓
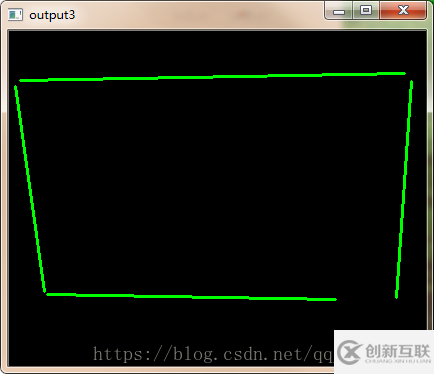
霍夫直線
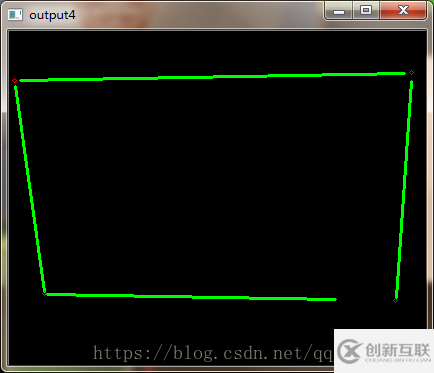
直線及其交點(diǎn)
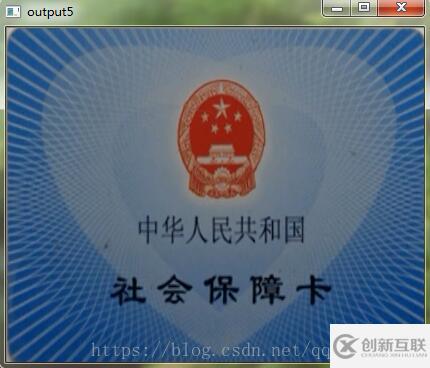
效果圖
以上是“Opencv中透視變換的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內(nèi)容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內(nèi)容對(duì)大家有所幫助,如果還想學(xué)習(xí)更多知識(shí),歡迎關(guān)注創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)行業(yè)資訊頻道!
本文題目:Opencv中透視變換的示例分析
本文路徑:http://www.chinadenli.net/article12/iehcgc.html
成都網(wǎng)站建設(shè)公司_創(chuàng)新互聯(lián),為您提供自適應(yīng)網(wǎng)站、網(wǎng)頁(yè)設(shè)計(jì)公司、搜索引擎優(yōu)化、小程序開(kāi)發(fā)、網(wǎng)站改版、做網(wǎng)站
聲明:本網(wǎng)站發(fā)布的內(nèi)容(圖片、視頻和文字)以用戶投稿、用戶轉(zhuǎn)載內(nèi)容為主,如果涉及侵權(quán)請(qǐng)盡快告知,我們將會(huì)在第一時(shí)間刪除。文章觀點(diǎn)不代表本網(wǎng)站立場(chǎng),如需處理請(qǐng)聯(lián)系客服。電話:028-86922220;郵箱:631063699@qq.com。內(nèi)容未經(jīng)允許不得轉(zhuǎn)載,或轉(zhuǎn)載時(shí)需注明來(lái)源: 創(chuàng)新互聯(lián)

- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航如何做優(yōu)化布局設(shè)計(jì) 2022-12-09
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)怎樣去設(shè)計(jì)一個(gè)合理的網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航 2016-04-09
- 設(shè)置對(duì)用戶有利的網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航 2021-08-10
- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航SEO優(yōu)化的5大要素 2015-12-19
- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航優(yōu)化的要點(diǎn)分別有哪些 2023-04-07
- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航建設(shè)如何遵循關(guān)鍵詞優(yōu)化技巧? 2022-08-04
- 如何優(yōu)化網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航結(jié)構(gòu)和恢復(fù)降權(quán)方法 2022-06-06
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)如何設(shè)計(jì)好網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航 2022-05-23
- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航 2021-06-14
- 網(wǎng)站建設(shè)良好的網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航把握以下幾點(diǎn)原則 2016-08-20
- 為什么很多SEOer非常注重網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航? 2015-05-13
- 網(wǎng)站導(dǎo)航是網(wǎng)站建設(shè)的重要一項(xiàng) 2022-09-25